I. The AI-Powered Touchless Revolution
1.1. Strategic Overview and Investment Catalyst
Wearable Devices Ltd. (WLDS), trading as NASDAQ: WLDS, is actively pioneering the next generation of human-computer interaction.1 The company develops a non-invasive neural input interface built into a wrist wearable band.3 This proprietary technology enables users to control digital devices using subtle finger movements.3 WLDS is classified as a growth company specializing in AI-powered neural input wearables.2
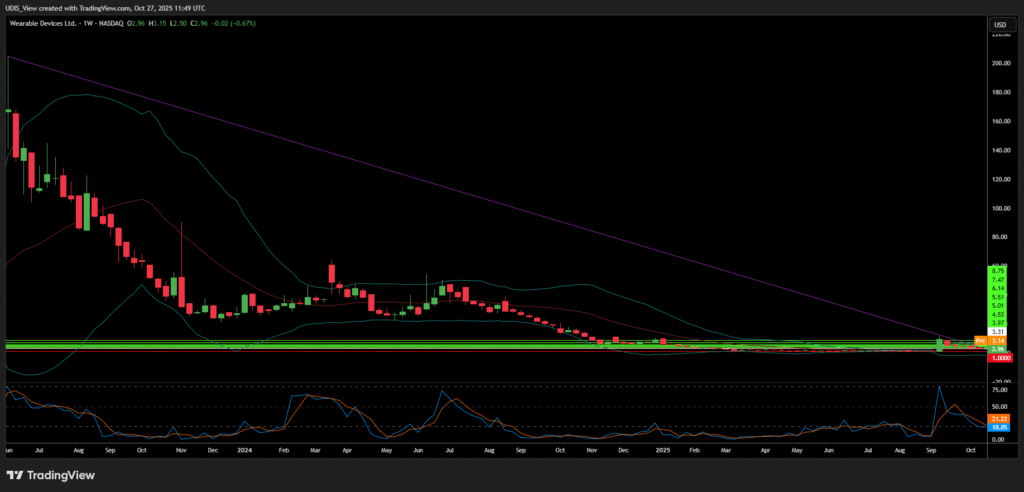
The primary catalyst driving current growth and market interest is a fundamental strategic shift in the company’s valuation model. 5 WLDS is transitioning from a reliance on consumer hardware sales, epitomized by the Mudra Band, to becoming an indispensable neural data intelligence platform.2 This pivot targets long-term, high-margin licensing revenue streams.2 The company’s stock exhibits high volatility, confirmed by a Beta of 3.58 and a 52-week range spanning $1.000 to $14.666.1 This volatility structure indicates that the current market valuation reflects anticipated future licensing revenue and market capture, rather than the company’s current revenue volume, which totaled $522,000 in 2024.7
WLDS holds a demonstrable first-mover advantage in AI-powered, wrist-based neural input.2 Its proprietary biosignal technology and expansive patent portfolio provide a critical competitive advantage.8 This technology positions WLDS to become the foundational neural backbone for the Extended Reality (XR) market and mission-critical defense sectors.2 The company’s potential as a major player in wearable neural interfaces is entirely dependent on successfully executing its long-term strategic phases focused on data monetization and ubiquitous platform adoption.2
1.2. Technology and Commercialization at a Glance
WLDS develops a unique, non-invasive technology, effectively addressing the complex safety and ethical barriers associated with invasive Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) surgery.10 The company utilizes a strategic dual-channel business model.11 This model effectively balances direct consumer product sales, which include the Mudra Band and Mudra Link, with lucrative enterprise licensing opportunities for OEMs and app developers.2
To accelerate global commercialization, WLDS actively pursues strategic collaborations.11 Partnerships with industry leaders such as Qualcomm, TCL-RayNeo™, and Media Exceed validate the technology’s readiness for mass integration and market scalability.2 The company further secures its position through an expanding intellectual property (IP) portfolio.2 This portfolio includes recent U.S. approvals covering advanced gesture-based and hybrid voice control technologies.13
II. The Technology Foundation: Neural Sensing and Working Method
2.1. Decoding Intent: WLDS’s Core Working Method
The core working method of WLDS relies on proprietary neural sensing technology and advanced AI algorithms.6 This system decodes subtle muscle signals and intent captured at the user’s wrist.6 The objective is to enable technology that listens deeply to human intent, adapting and integrating seamlessly into daily life.6 The flagship products, the Mudra Band and Mudra Link, feature a high-resolution analog front end and an integrated Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU).2 This combined hardware and adaptive machine learning approach delivers the necessary low-latency and high-accuracy performance for immersive interactions, such as those in the XR environment 2
The company’s long-term technological vision culminates in the Large Motor-Unit Action Potential Model (LMM).2 This bio-signal intelligence platform is designed for continuous learning and adaptation.2 By 2026, the system is expected to transition beyond interpreting discrete inputs to enabling continuous neuromuscular monitoring.6 Critically, every interaction is captured as high-resolution neural input, which is structured into a proprietary bio-signal dataset.6 This proprietary dataset is fundamental to training the LMM, positioning the platform as an integrated system that learns from real-world biosignals, forming the basis for the Neural Data Intelligence Platform 6
2.2. Technological Moat: Neural Input vs. sEMG
The non-invasive neural interface sector is characterized by several distinct technologies.15 Highly invasive BCIs, despite offering the highest signal fidelity, require surgery and face major challenges related to user acceptance and biological compatibility.10 Non-invasive alternatives, such as EEG headbands, often have inherent limitations in signal resolution.15 The most direct commercial competition comes from wrist-based Surface Electromyography (sEMG) solutions, exemplified by Meta’s products designed for their display glasses ecosystems.17
Meta’s documentation explicitly states that sEMG operates peripherally, sensing electrical signals solely from muscle activations.18 It does not sense neural signals originating from the brain.18 WLDS’s key technical differentiation lies in its proprietary classification as a “Neural input interface”.3 Its critical patents support the capability to measure weight, torque, and applied force directly from the wrist sensors.8 This functional claim implies a more advanced and refined signal decoding process than basic sEMG gesture recognition. Standard sEMG is generally limited to detecting muscle output patterns.18 The capability to quantify physical forces, such as the torque applied when rotating machinery components, validates WLDS’s claim of advanced bio-signal decoding.14 This high-fidelity input allows WLDS to secure a technical niche, enabling it to penetrate demanding, high-precision industrial and professional markets that basic sEMG devices cannot reliably address.8
2.3. The Future: Moving Beyond Control
The company’s roadmap dictates continuous technological advancement.2 Phase 3 explicitly focuses on leveraging the accumulated neural data to open new verticals, shifting the application from device control to user state understanding.2 A significant new vertical is digital health and predictive health monitoring.2
The LMM platform is designed to utilize muscle activation signals to detect patterns related to stress, fatigue, focus, and potential early signs of health irregularities.2 These signals could flag neuromuscular irregularities before traditional symptoms become manifest.2 By developing solutions for workplace productivity (alertness monitoring) and preventive healthcare, the LMM platform substantially expands WLDS’s addressable market beyond consumer electronics.2 This strategy ensures the technology evolves to both control external devices and provide actionable bio-insights by continuously adapting to each individual’s neural profile.2
III. The Fortress of IP: Patent Portfolio and Defense
3.1. Securing the Neural Frontier: Patent Overview
Wearable Devices Ltd. strategically protects its foundational technology through a growing portfolio of granted and pending patents globally.6 The IP strategy is designed to cover key innovations across multiple layers, including hardware design, algorithm development for signal processing, and methods for real-time interaction.6
The company has secured multiple U.S. patents that underpin its commercial products.13 These patents include protection for realistic gesture-controlled virtual object modulation.3 Furthermore, a significant patent covers a breakthrough hybrid voice and gesture-controlled interface, which incorporates biometric authentication for enhanced security.13 The portfolio also includes a method for extracting precise start and end points from continuous gestures.19
3.2. Quantitative IP: Measuring Force and Torque
WLDS’s most essential patents reinforce its technological advantage by moving beyond simple gesture detection.8 These patents specifically cover the neural measurement of weight, torque, and force.13 This quantitative capability is critical for securing market leadership in high-fidelity sensing fields.8
Specific patent claims detail the ability to estimate the weight of objects and measure the torque applied when rotating items like screws or faucets.14 They also quantify applied force, which is necessary for quality control applications, such as securing cable harness connectors in Industry 4.0 environments.14 These claims ensure WLDS dominates the IP space related to quantifiable, force-based neural measurement, with applications spanning Extended Reality (XR) embodiment and general Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI).14 This patent strategy creates a crucial technical barrier, establishing an IP moat around specialized professional and industrial use cases.8 The robust nature of these patents validates the technological superiority claimed by the company, positioning it as an essential licensor for future high-value enterprise partners.
IV. Strategic Execution: Phased Commercialization and Customer Base
4.1. The Dual-Channel Business Model and Customers
WLDS utilizes a highly efficient hybrid dual-channel business model.2 This model is predicated on B2C product sales for rapid market seeding and user data collection, combined with B2B enterprise licensing for scale and recurring revenue.2
The customer base reflects this bifurcated strategy.12 B2C customers include tech enthusiasts and early adopters, particularly within the Apple ecosystem, using the Mudra Band.2 The Mudra Link extends this access to users on Android, PC, and XR headset platforms.12 B2B customers consist of enterprises, OEMs, and application developers seeking to integrate the neural input technology into their commercial products.2 Current strategic partners, including Qualcomm, TCL-RayNeo™, and Media Exceed, serve as critical B2B validation points, supporting efforts to scale commercialization globally.11
4.2. Support and Funding Ecosystem
The company receives crucial logistical and commercial support through its strategic alliances.11 Partnerships with major players like Qualcomm provide essential validation and pathways for integration into mobile and chipset ecosystems.2 The alliance with TCL-RayNeo™ is instrumental for market entry and scaling, particularly in the rapidly growing AR/XR hardware sector.2
Financial support is evidenced by institutional ownership.20 Institutional investors listed in filings include Kathmere Capital Management LLC, Armistice Capital LLC, and Virtu Financial LLC.20 The ongoing interest from these entities suggests market confidence in the company’s ability to execute its long-term platform strategy.21
4.3. The 4-Phase Roadmap: Short and Long Term
The strategic plan is structured into a measured, four-phase trajectory, guiding the transition from direct-to-consumer sales to ubiquitous data infrastructure licensing.2 Phase 1, Enthusiast Consumer Adoption, achieved market validation through the Mudra Band 2
The current focus is the short-term goal of Phase 2: Platform Expansion.2 This involves the launch of the Mudra Link and the opening of the Mudra SDK to developers, which is crucial for accelerating integration into enterprise and XR use cases.2
Long-term success relies on Phases 3 and 4.2. Phase 3 (Mid-Term, expected post-2026) involves leveraging the data set by activating the LMM platform for continuous neuromuscular monitoring.2 The objective is to establish a proprietary bio-signal data bank and monetize it through high-margin licensing, particularly targeting predictive health and cognitive analytics.2 The ultimate long-term milestone, Phase 4, is Ubiquitous Adoption via B2B Integration.2 In this phase, WLDS aims to align with major consumer tech giants, positioning the Mudra Data Platform as the mature, data-rich industry standard for neural interaction services.2 The necessity of B2C sales to generate the proprietary data required to train the LMM platform highlights how consumer adoption directly fuels the company’s high-margin enterprise business.2
WLDS Strategic Roadmap and Value Drivers
| Phase | Timeline | Primary Focus | Key Value Driver |
| Phase 1: Enthusiast Adoption | Current/Past | B2C, Apple Watch (Mudra Band) sales | Proof-of-Concept, Initial Revenue, Data Seeding 2 |
| Phase 2: Platform Expansion | Short-Term | Mudra Link Launch, Mudra SDK Release; Focus on XR/AR | Ecosystem Growth, Scaling into Enterprise Use-Cases via Developer Kit 2 |
| Phase 3: Data & Verticals | Mid-Term (Post-2026) | LMM Platform Activation; Continuous Neuromuscular Monitoring | Proprietary Bio-Signal Data Bank, High-Margin Licensing, Predictive Health 2 |
| Phase 4: Ubiquitous Integration | Long-Term | OEM Alignment; Mass B2B Licensing via Mudra Data Platform | Positioned as the industry standard for neural interaction services 2 |
V. Macroeconomic and Geostrategic Drivers
5.1. Macroeconomics and High-Tech Growth
WLDS’s current growth is fundamentally driven by robust macroeconomic and high-tech market trends.22 The global Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) market is expanding rapidly, projected to grow from $1.74 billion in 2022 to $6.2 billion by 2030, representing a 17.5% CAGR.22 The wireless neural interfaces industry forecasts a strong 15.2% CAGR through 2035.23
This exponential market growth is propelled by increasing consumer demand for non-invasive BCI solutions across gaming, consumer electronics, and productivity applications.22 The market is rapidly shifting toward mass commercialization of neurotechnology.22 WLDS benefits by aligning its focus on the two fastest-growing application segments: Extended Reality (XR) and digital health monitoring.2 Its position as a first-mover with a mature, cross-platform solution allows it to capture this escalating demand.2
5.2. Geopolitics and Geostrategy: Defense Validation
WLDS’s proprietary technology holds significant geostrategic value, extending its applications into critical sectors.9 The company is currently developing a neural interface for advanced military tactical systems.9 This solution allows soldiers to interact with control and communication devices using intuitive gestures.9 This hands-free control is vital for maintaining tactical readiness and flexibility in modern warfare scenarios.9
Engagement in military projects serves to strongly validate the technology’s robustness.25 Successful deployment in mission-critical and extreme environments provides independent evidence of the platform’s reliability and security.25 This high level of technical validation significantly de-risks the technology for subsequent commercial adoption.25 Proving its utility in defense accelerates acceptance across related high-risk fields, such as industrial safety and emergency response, reinforcing the B2B licensing pitch for high-value enterprise clients.25
5.3. Cyber Risks in the Neural Era
The swift introduction of neural interfaces into the mass market presents profound cybersecurity risks.26 Wearable devices already collect highly sensitive data, including biometric details and behavioral patterns.27 Brain-Computer Interfaces amplify these concerns, introducing the potential for “eavesdropping on neurological data” or, critically, the malicious manipulation of neural activity 26
Existing regulatory structures, including data protection laws and medical device regulations, have significant gaps concerning cyberattacks on BCIs.26 Given WLDS’s commitment to military applications 9 and its emphasis on collecting proprietary, high-resolution data via the LMM 2, platform security is paramount. For the high-value B2B licensing model (Phase 4) to be successful, robust security, encryption, and data integrity protocols must be integrated as core, competitive features of the Mudra Data Platform.27 This approach converts an inherent industry risk into a powerful differentiator for enterprise partnerships.
VI. Competition, Market Share, and Capacity
6.1. Capacity and Scalability
WLDS operates under a lean operational capacity structure.28 The employee headcount ranges between 26 and 34 individuals.28 The company maintains its headquarters in Yokneam Illit, Israel, and recently established a vital strategic presence in Silicon Valley to strengthen relations with North American partners 29
This small physical capacity structurally mandates a focus on a low-Capex business model.2 WLDS is not built to compete on mass manufacturing volume.31 Instead, its resources are concentrated on high-value intellectual assets: IP generation, advanced AI development (LMM), and technical support for B2B integration (SDK/Licensing).2 The valuation hinges on the quality of its technological platform and IP, rather than production scale.1
6.2. Global BCI Market and Competitor Output
WLDS is positioned to become a major player in wearable neural interfaces by targeting the significant gap between technological potential and current market penetration.32 While the need for wireless neural interfaces is escalating rapidly, analyst projections suggest BCI revenues will reach only about $1.5 billion by 2035.23 This modest revenue forecast, relative to the projected market potential, indicates a substantial unmet need, particularly for non-invasive, mature consumer solutions.7
Major competitors in the broader BCI space include Neuralink and Synchron, which focus on highly invasive, high-fidelity medical applications.23 Non-invasive alternatives include Emotiv and NeuroSky, which specialize in cognitive monitoring.23 The most direct technological challenge comes from wrist-based solutions like Meta’s sEMG technology.17 WLDS’s proprietary neural input, secured by IP covering force and torque measurement, provides a quantitative technical advantage over generalized sEMG, allowing it to address higher-specification control applications.14
6.3. Penetrating the Asia-Pacific Market
The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth in the global wearable technology market, with a projected CAGR exceeding 15% through 2030.5 This expansion is driven by robust R&D, government initiatives in digital healthcare, and a burgeoning middle class in countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea.5
Competitors dominating the Asian consumer wearable market share include ecosystem giants like Huawei, Xiaomi, Samsung, and Sony.31 These firms command the consumer landscape, with smartwatches alone claiming 46% of the overall wearable market share.33 WLDS’s direct consumer market share in Asia is currently small, consistent with its strategic focus on platform development.7
WLDS intends to capture market share by pursuing strategic B2B integration.2 The partnership with TCL-RayNeo™ is a critical geo-specific strategy.11 TCL, a key Asian consumer electronics player, enables WLDS to embed its neural technology directly into high-growth hardware segments like AR/XR headsets.12 By licensing the Mudra Data Platform for ubiquitous adoption (Phase 4), WLDS bypasses the need for high capital expenditure and direct competition against local giants on hardware price and volume.2 Asia-Pacific expansion is therefore contingent upon securing multiple, high-volume OEM licensing agreements.
VII. Conclusion: A Platform Play in the Neural Frontier
Wearable Devices Ltd. is executing an assertive strategic pivot designed to capitalize on the neurotechnology revolution.22 The company’s increased growth across multiple domains is fundamentally driven by its transition from a consumer hardware provider to a proprietary neural data intelligence platform (LMM).2
The company’s technological advantage is quantifiable and secured by robust IP.13 Critical patents covering the measurement of force, torque, and hybrid gesture-voice control demonstrate a superior fidelity compared to standard sEMG competitors.8 This IP moat ensures WLDS remains relevant in both high-growth consumer XR and mission-critical geopolitical applications.8
WLDS can be a major player in wearable neural interface development.7 Its success hinges entirely on the execution of its strategic roadmap: successful consumer adoption (Phase 1/2) must yield the necessary data to train and monetize the LMM platform (Phase 3), thereby enabling ubiquitous enterprise licensing (Phase 4).2 By aligning its dual-channel business model and small operational capacity with high-margin licensing, WLDS is positioning itself as the infrastructure backbone necessary for the mass adoption of touchless human-computer interaction.2
Refferences
- Wearable Devices (WLDS) Stock Price & Overview
- Wearable Devices Ltd. (NASDAQ: WLDS) – IBN (InvestorBrandNetwork)
- Investors | Wearabledevices
- IR events & presentation | Wearabledevices
- Neural Interface Wearable Devices Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
- Wearable Devices
- Wearable Devices Ltd. (NASDAQ: WLDS) Strengthens Mudra Neural Technology, Blazes the Trail in AI-Wearables Market — Positioned as the Universal Alternative to Proprietary Neural Band – NetworkNewsWire
- Wearable Devices Ltd. (NASDAQ: WLDS): How Neural Interface Patents Are Securing the Future of Touchless Control – TechMediaWire
- Wearable Devices Announces Development of Neural Interface for Advanced Military Tactical Systems
- The Neural Interface and Its Evolving Role in XR – XR Today
- Wearable Devices Ltd.
- About| Wearabledevices
- IR Press | Wearabledevices
- Wearable Devices Secures U.S. Patent for Groundbreaking Neural Interface Technology
- A New Path to Noninvasive Brain-Computer Interface – Johns Hopkins APL
- New Wearable Brain-Computer Interface – Georgia Tech Research
- EMG Wristbands and Technology – Meta Store
- Human-Computer Input via a Wrist-Based sEMG Wearable | Meta Quest Blog
- Wearable Devices Receives U.S. Patent for Innovative Gesture Control, Enabling Precision Interaction with Digital Devices – GlobeNewswire
- Wearable Devices (WLDS) Institutional Ownership 2025 – MarketBeat
- WLDS – Wearable Devices Ltd. Stock – Stock Price, Institutional Ownership, Shareholders (NasdaqCM) – Fintel
- The brain-computer interface market is growing – but what are the risks?
- Wireless Neural Interfaces Market Insights 2025 to 2035
- Brain-computer Interface Smart Wearable Devices Unlocking Growth Opportunities: Analysis and Forecast 2025-2033 – Market Insights Report
- Wearable Devices Ltd. Expands Neural Interface Technology for Military Applications
- [Cybersecurity of brain-computer interfaces] – PubMed
- Dangers of Wearable Tech: CyberSecurity Insights – Southridge Technology
- Wearable Devices 2025 Company Profile: Stock Performance & Earnings | PitchBook
- Wearable Devices Ltd (WLDS) Profile, Company FAQs & Facts, Industry, Sector, Employee Strength
- Wearable Devices Establishes U.S. Offices in Silicon Valley, Expanding North American Presence
- Wearable Technology Market Size | Industry Report, 2030 – Grand View Research
- Top 10 Brain-Computer Interface Companies in 2025 – Spherical Insights
- Wearable Technology Market Size, Share & Trends Report 2030 – Mordor Intelligence
Wearable Devices Long (Buy)
Enter At: 3.31
T.P_1: 3.97
T.P_2: 4.53
T.P_3: 5.01
T.P_4: 5.51
T.P_5: 6.14
T.P_6: 7.47
T.P_7: 8.75
S.L: 1.00