The Convergence of Domains
Karman Space & Defense (NYSE: KRMN) has executed a definitive strategic maneuver that fundamentally redefines its market position. The company announced an agreement to acquire Seemann Composites and Materials Sciences LLC (MSC) for $220 million. This transaction is not merely a capacity expansion. It represents a calculated pivot into the high-stakes domain of maritime superiority.
Karman is aggressively moving beyond its stronghold in space and missile systems. The acquisition targets the U.S. Navy’s most critical modernization priorities: the submarine industrial base and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). This move effectively creates a vertically integrated prime contractor capable of delivering survivability solutions from the ocean floor to orbit.
The deal structure is precise. Karman will deploy $210 million in cash and approximately $10 million in equity to close the transaction. Management anticipates the deal will close in the first quarter of fiscal year 2026. The acquisition is projected to be immediately accretive to revenue, EBITDA, and earnings per share.
This report provides an exhaustive analysis of this strategic pivot. We examine the convergence of aerospace and maritime material sciences, analyze the geopolitical imperatives driving the “Department of War” (DOW) investments, and dissect the patent portfolios that underpin Karman’s new competitive moat.
Transaction Mechanics and Valuation
The following table outlines the core financial structure of the acquisition:
| Metric | Detail |
| Acquirer | Karman Space & Defense (NYSE: KRMN) |
| Target Entities | Seemann Composites & Materials Sciences LLC (MSC) |
| Total Consideration | $220 Million |
| Cash Component | $210 Million |
| Equity Component | ~$10 Million (Karman Common Stock) |
| Target Capabilities | Advanced Composites, Acoustic Damping, SCRIMP™ Manufacturing |
| Strategic Rationale | Entry into Submarine Industrial Base & Unmanned Systems |
| Closing Timeline | Q1 Fiscal Year 2026 |
| Financial Impact | Immediately Accretive to Revenue, EBITDA, EPS |
Geopolitics: The Indo-Pacific Imperative
The strategic logic driving this acquisition is rooted in the escalating great power competition in the Indo-Pacific. The United States faces a “near-peer” adversary challenge that necessitates a fundamental shift in naval architecture.
The Acoustic Arms Race
The balance of power in the Pacific theater hinges on undersea warfare. China’s People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) is rapidly modernizing its submarine fleet. The deployment of Type 039A/B “Yuan” class submarines introduces a significant threat. These vessels utilize Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) systems. AIP allows conventional submarines to remain submerged for weeks without snorkeling. This capability drastically reduces their acoustic and thermal signatures.
The noise gap between U.S. nuclear submarines and Chinese diesel-electric boats is narrowing. This reality forces the U.S. Navy to prioritize “acoustic superiority” above all other metrics.
The A2/AD Asymmetric Challenge
China has established formidable Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) zones. These zones utilize dense networks of hydro-acoustic sensors and active sonar arrays to deny U.S. forces freedom of maneuver. Traditional metallic hulls reflect sonar energy, making them visible to these sensor networks.
To penetrate these zones, U.S. platforms must become acoustically invisible. This requires a transition from metal to advanced composites. Seemann Composites provides the “bow-to-stern” solutions necessary to achieve this stealth. Their materials absorb rather than reflect sound energy, enabling U.S. assets to operate inside the A2/AD bubble.
Department of War Priorities
The acquisition aligns Karman directly with the specific mandates of the U.S. Department of War (DOW). The DOW has identified the “submarine industrial base” as a critical fragility point. The operational requirement to build one Columbia-class and two Virginia-class submarines annually places immense strain on existing supply chains.
Karman is stepping into this breach. Seemann’s 240,000 square feet of manufacturing capacity provides the industrial surge capability the DOW demands. By securing this capacity, Karman positions itself as a “national champion” in defense composites.
Geostrategy: Controlling the Undersea Domain
Geostrategy dictates that control of the seas requires control of the sub-surface. The acquisition of Seemann Composites allows Karman to equip the platforms that will secure this control.
The Strategic Shift to Unmanned Systems
The future of naval combat is unmanned. The Navy is heavily investing in Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) and Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs). These platforms must be autonomous, enduring, and stealthy.
- Endurance: Composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to steel. Lighter hulls allow for larger battery payloads and longer mission durations.
- Stealth: Unmanned systems operating in contested waters cannot rely on speed. They must rely on low observability. Seemann’s materials provide the acoustic damping required for survival.
Protecting the Nuclear Deterrent
The Columbia-class ballistic missile submarine is the nation’s top priority defense program. It ensures the survivability of the sea-based leg of the nuclear triad. Seemann Composites is a critical supplier to this program. Karman now holds a stake in the most vital strategic asset in the U.S. arsenal. This guarantees revenue stability for decades, as the Columbia program is insulated from typical budgetary volatility due to its strategic importance.
Macroeconomics: The Fiscal Defense Landscape
The fiscal environment for defense contractors in 2026 is robust. The DOW budget reflects a wartime footing, prioritizing readiness and industrial capacity.
Budgetary Tailwinds and Program Stability
The 2026 defense budget allocates significant funding to shipbuilding and modernization:
- Columbia Class: Fully funded to ensure continuous strategic deterrence.
- Virginia Class: Continued procurement of Block V boats with acoustic superiority upgrades.
- Industrial Base Support: Direct investments, such as the $32.7 million for solid rocket motors (SRM), demonstrate DOW’s willingness to subsidize critical suppliers.
Karman’s revenue exposure is now tied to these “multi-decade, funded programs”. This shifts the company’s risk profile from the volatile commercial space launch market to the predictable, long-cycle defense market.
Inflation and Cost Dynamics
Defense programs are sensitive to inflation. Fixed-price contracts can erode margins if input costs rise. However, the shift to composites offers a hedge.
- Corrosion Resistance: Composites do not corrode. This reduces lifecycle maintenance costs for the Navy, making Seemann’s products a deflationary force for the customer.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Seemann’s proprietary SCRIMP process reduces labor and energy costs compared to traditional autoclave curing. This efficiency protects margins even in an inflationary environment.
Private Equity and Capital Markets
Karman is backed by Trive Capital. The acquisition strategy reflects a classic private equity “buy-and-build” playbook. By aggregating niche suppliers into a Tier 1 prime, Trive creates a platform that commands a higher valuation multiple (Multiple Arbitrage). This diversification into maritime defense makes Karman a more attractive target for eventual acquisition by a massive prime (e.g., General Dynamics) or for a secondary offering.
Economics: Vertical Integration and Value Capture
Karman’s strategy is explicitly “concept-to-production”. The economic logic is to capture value at every stage of the supply chain.
The Integrated Margin Stack
The acquisition creates a vertically integrated manufacturing stack that captures margin at three distinct levels:
- Raw Materials (Level 1): Karman owns the proprietary resin formulations (MG Resins).
- Engineering (Level 2): MSC provides the design, analysis, and testing services.
- Manufacturing (Level 3): Seemann provides the large-scale production capability.
By controlling all three levels, Karman eliminates “double marginalization.” They do not pay a markup to a resin supplier or a design firm; they keep that profit in-house.
Supply Chain Resilience
The DOW prioritizes supply chain resiliency. Vertical integration reduces dependence on external vendors. Karman can now guarantee delivery timelines to the Navy because it controls its own inputs, a reliability that commands a premium price in government contracting.
Technology: The Material Science of Stealth
The core value of this acquisition lies in the intellectual property and manufacturing technologies. Seemann and MSC are not generic fabricators; they are deep-tech innovators.
SCRIMP: Revolutionizing Composite Manufacturing
The Seemann Composites Resin Infusion Molding Process (SCRIMP) is the technological foundation of the company. Traditional composite manufacturing requires expensive autoclaves (pressurized ovens) to eliminate air bubbles, limiting the size of parts.
The SCRIMP solution uses a VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) process that utilizes atmospheric pressure to infuse resin. A patented distribution medium flows resin quickly across the surface and then down into the fiber. This enables the production of massive, void-free structures like entire submarine bow domes at a fraction of the cost.
Acoustic Metamaterials
MSC possesses expertise in acoustic metamaterials. These are engineered structures designed to manipulate sound waves in ways not found in nature. Patent US11498282B1 describes materials with embedded micro-resonators that can be tuned to absorb specific frequencies. This allows Karman to build submarine coatings that perfectly match the frequency of enemy active sonar; the sonar ping is absorbed, and no echo returns.
High-Temperature Ablatives
Karman’s existing MG Resin technology creates carbon-carbon composites that withstand temperatures above 1200°C. While these materials form the heat shields and nose cones of hypersonic missiles, the chemistry knowledge required to resist 1200°C heat is complementary to the knowledge required to resist deep-sea pressure. Karman can now cross-pollinate these resin technologies.
Cyber: Smart Skins and Digital Twins
The “Cyber” domain in this context refers to the integration of digital sensing into physical structures. MSC integrates fiber optic sensors directly into the composite matrix.
Using High-Definition Fiber Optic Sensing (HD-FOS), this technology turns a passive hull into an active sensor (“Smart Skin”) that can “feel” strain, pressure, and temperature. This sensor data feeds into the ship’s central processor, creating a real-time “Digital Twin” of the vessel.
This has immense implications for the DOW’s “Project Overmatch.” It provides real-time diagnostics, allowing commanders to push platforms to their limits. Karman is effectively selling hardware that generates valuable cyber data, increasing the “stickiness” of their products.
Science: Physics of the Deep
Seemann’s composites enable complex hydrodynamic shapes that are impossible with metal. Smooth, joint-free composite structures reduce drag and flow noise, contributing to acoustic stealth.
Furthermore, MSC utilizes advanced algorithms to predict the fatigue life of composites. Since composites delaminate rather than crack, MSC’s adaptation of the “R.R. Moore Rotating Beam Test” allows for rapid high-cycle fatigue testing (up to 10^9 cycles), giving the Navy confidence to certify composites for critical structural applications.
High-Tech: Advanced Manufacturing
Karman is deploying Industry 4.0 technologies to scale production, including Automated Fiber Placement (AFP). Robots place fiber tape with millimeter accuracy, offering speed and repeatability critical for meeting “SUBSAFE” requirements.
The deal also includes 3D printing capabilities for complex parts. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of internal lattice structures in parts, optimizing weight and stiffness.
Patent Analysis: The Intellectual Property Moat
A detailed analysis of the patent portfolio reveals the depth of Karman’s competitive advantage.
| Patent ID | Title | Strategic Relevance |
| US 5,958,325 | Large Composite Structures… | Foundation of the SCRIMP process. Enables large-scale naval manufacturing. |
| US 6,773,655 | Method for Production… | Refinement of VARTM. Ensures void-free quality for submarine hulls. |
| US 11,498,282 | Acoustic Metamaterials | Optimization of micro-resonators for acoustic stealth. Critical for A2/AD penetration. |
| US 8,028,800 | Acoustic Damping Compositions | Chemical formulations for sound absorption. Basis for anechoic coatings. |
| US 7,408,842 | Sonar Dome | Specific design IP for sonar domes. Directly monetizable on naval vessels. |
These patents create a formidable barrier to entry. Competitors cannot easily replicate the SCRIMP process or the specific acoustic metamaterial designs without infringing on Karman’s IP.
Financial Analysis: Balance Sheet and Guidance
Karman reported robust growth, with record revenue of $345.3 million in 2024 (up 23% YoY) and Q3 2025 revenue hitting $121.8 million (up 41.7%). Their funded backlog reached $758.2 million in Q3 2025, providing exceptional visibility, while Q3 2025 EBITDA stood at $38 million (31% margin).
However, some analysts have flagged concerns regarding “unbilled revenue,” which exceeds 43% of reported revenue. While this suggests revenue is recognized before cash is collected, the high percentage of government contracts and robust backlog support ultimate collectability. The “immediately accretive” cash flow from Seemann will help alleviate this working capital strain.
Regarding leverage, Karman increased its Term Loan B to $505 million to fund acquisitions. The debt-to-equity ratio sits around 1.31. With ~$27 million in cash at the end of Q2 2025, the company is relying on its expanded debt facility, making execution paramount.
Future Outlook: The 2030 Roadmap
Karman’s trajectory points towards becoming a diversified “Super-Prime” supplier. The immediate focus will be on integrating Seemann’s Gulfport, MS operations with Karman’s West Coast HQ, with the retention of Seemann’s leadership team mitigating cultural risks.
Looking to 2030, the AUKUS partnership and Australia’s acquisition of nuclear submarines offer massive international opportunities. The convergence of thermal and structural composites positions Karman to lead in the hypersonic glide vehicle market, while their acoustic damping tech will be vital for protecting next-gen satellite constellations during launch.
Conclusion
Karman Space & Defense has executed a masterstroke of industrial strategy. The acquisition of Seemann Composites transforms the company from an aerospace parts supplier into a multi-domain defense powerhouse. By aligning with the “Department of War’s” most urgent priorities undersea warfare and supply chain resilience, Karman ensures its relevance for decades. The technological synergies between space-grade ablatives and marine-grade composites create a unique “Deep Sea to Deep Space” capability that no peer can match. Karman is no longer just watching the stars; it is now patrolling the depths.
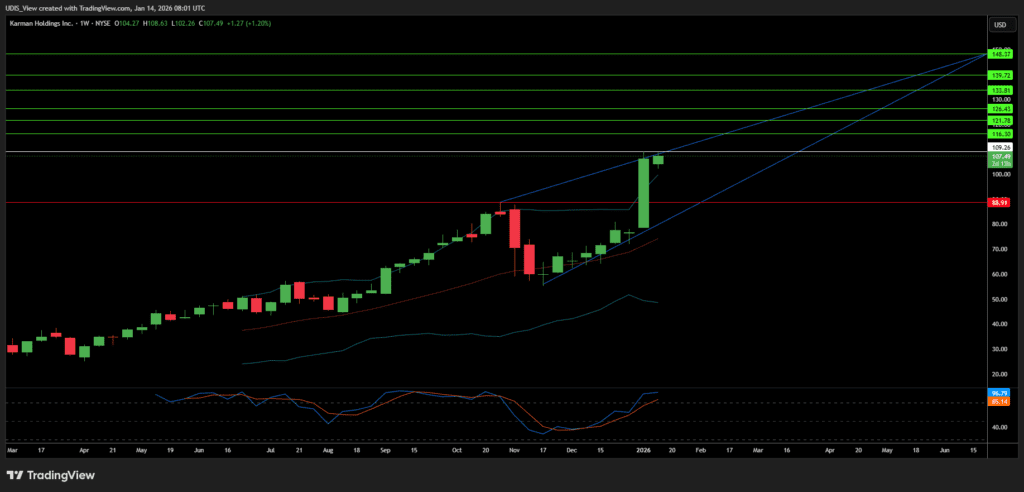
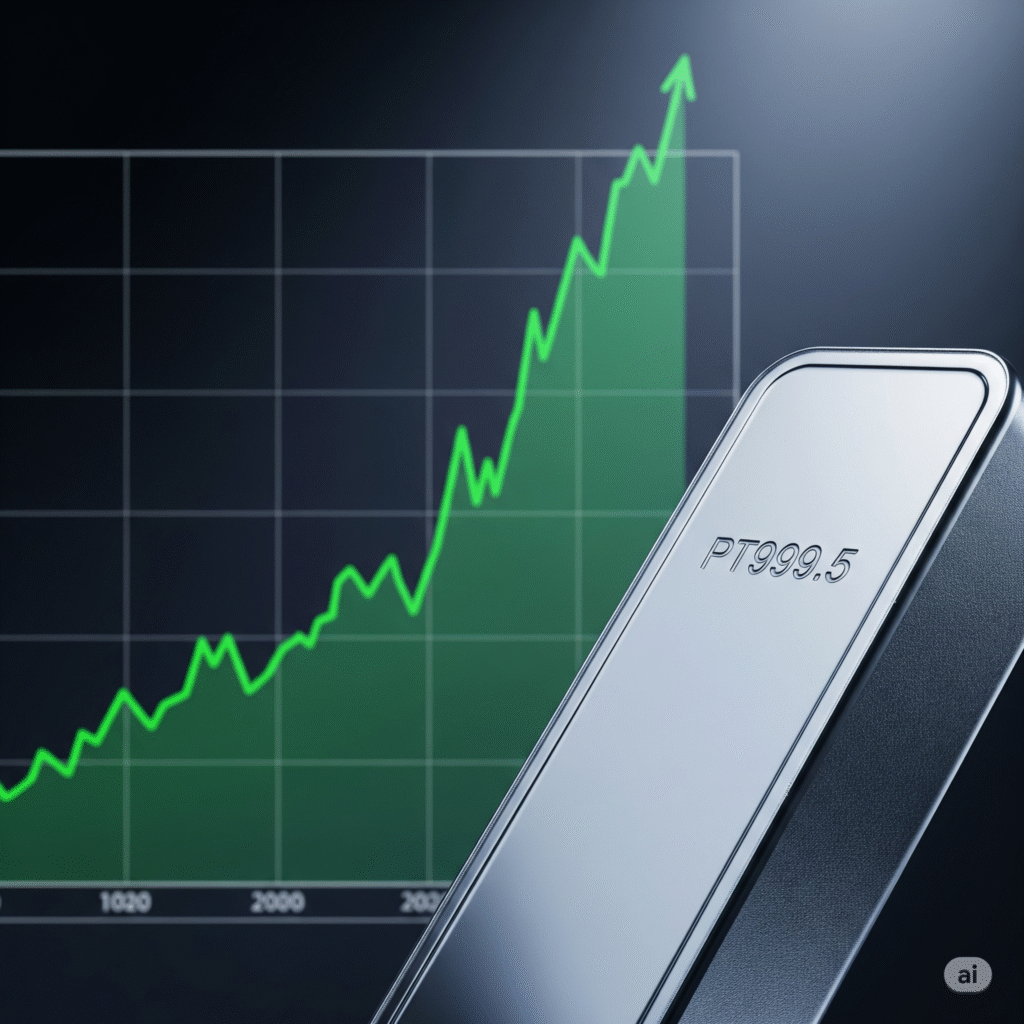
Karman Long (Buy)
Enter At: 109.26
T.P_1: 116.30
T.P_2: 121.78
T.P_3: 126.43
T.P_4: 133.81
T.P_5: 139.72
T.P_6: 148.37
S.L: 88.91