GE Aerospace has emerged as a formidable independent entity, shedding its conglomerate past to focus on core aviation strengths. This strategic transformation, completed with its spin-off, has unlocked significant value. The company’s ascent is not merely a result of internal restructuring. It reflects a powerful confluence of global geopolitical shifts, a robust macroeconomic recovery in commercial aviation, and strategic technological innovation. GE Aerospace’s dual commercial and defense market presence, coupled with its deep installed base and aftermarket services, positions it uniquely to capitalize on these evolving dynamics. Its ability to navigate complex trade landscapes and lead in sustainable aviation further solidifies its market leadership.
A New Era for GE Aerospace
A. The Genesis of Independence
General Electric embarked on a multi-year transformation, strategically divesting its diverse segments to create focused, independent companies. This culminated in the spin-off of GE Aerospace, marking a pivotal moment in its history 12. The move was designed to unlock substantial shareholder value by allowing GE Aerospace to concentrate solely on its core aviation business. This strategic unbundling enhances organizational agility and provides clearer capital allocation for its high-margin segments. The separation allows investors to evaluate GE Aerospace based purely on its aerospace fundamentals, removing the “conglomerate discount” that often weighed on GE’s stock. This focused approach facilitates more efficient resource deployment into critical areas like propulsion technology and aftermarket services.
B. Market Position and Core Strengths
GE Aerospace stands as a leading global supplier of aircraft engines for both commercial and military applications 3. A vast installed base of engines worldwide underpins its market dominance. This extensive fleet generates substantial, high-margin revenue through aftermarket services, including maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) 4. The company’s dual presence in commercial and military segments provides inherent resilience. This diversified exposure mitigates risks associated with downturns in any single sector. Furthermore, GE Aerospace maintains technological leadership in advanced propulsion systems, a critical competitive advantage. The long lifecycle of aircraft engines ensures a steady stream of service revenue, providing stability against the cyclical nature of new aircraft deliveries.
Geopolitical and Geostrategic Tailwinds
A. Escalating Global Tensions and Defense Spending
Current global dynamics significantly bolster GE Aerospace’s defense segment. Nations worldwide are increasing defense budgets in response to heightened geopolitical instability. The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has particularly spurred rearmament efforts across Europe and beyond. NATO expansion and the renewed focus on collective defense have driven significant investment in military capabilities. This environment creates sustained demand for GE Aerospace’s advanced military aircraft engines and systems 3. The persistent global tensions ensure a robust order book for GE Aerospace’s defense division, providing a reliable and predictable revenue stream that helps balance potential fluctuations in the commercial market.
B. Geostrategic Importance of Aviation Technology
Aerospace technology plays a critical role in national security and power projection. GE Aerospace’s position as a key defense supplier makes it an indispensable part of global defense supply chains. The company’s focus on developing cutting-edge propulsion systems is vital for next-generation military aircraft(https://www.geaerospace.com/news/ge-reports/ge-aerospaces-f404-little-engine-could-and-still-does). This strategic importance often translates into robust government partnerships and consistent R&D funding for critical programs. Being a cornerstone defense supplier grants GE Aerospace a unique strategic status. This can lead to preferential treatment in government contracts, access to significant research and development funds, and a degree of insulation from certain economic or trade pressures, further strengthening its market position.
Macroeconomic Resurgence and Commercial Aviation Recovery
A. Post-Pandemic Travel Rebound
The global air travel sector has experienced a strong and sustained recovery following the pandemic downturn. This resurgence in passenger demand directly translates into increased flight hours for commercial aircraft 4. Higher flight utilization, in turn, significantly boosts demand for GE Aerospace’s lucrative aftermarket services, including engine maintenance and spare parts 4. Airlines are reporting improved profitability, enabling them to pursue fleet modernization and expansion plans. The robust rebound, particularly in international travel, underscores pent-up demand and a fundamental human need for connectivity. This strong recovery provides a powerful tailwind for GE Aerospace’s commercial engine and services segments, driving significant revenue growth.
B. Supply Chain Dynamics and Production Ramp-up
The aerospace industry has faced considerable supply chain challenges, including labor shortages and material delays. GE Aerospace has actively implemented strategies to mitigate these disruptions, working closely with suppliers to stabilize production. These efforts are crucial as the company ramps up engine production rates to meet surging demand for new aircraft 5. Navigating these complexities effectively impacts delivery schedules and overall profitability. While supply chain bottlenecks present short-term hurdles, GE Aerospace’s proactive management demonstrates its operational resilience. Successfully overcoming these challenges allows the company to fully capitalize on the sustained demand for new aircraft and engine deliveries, converting orders into revenue.
C. Inflationary Pressures and Pricing Power
Inflationary pressures have impacted input costs across various industries, including aerospace. GE Aerospace employs strategic pricing mechanisms to manage these rising costs. Its long-term contracts for engine sales and aftermarket services often include escalation clauses or allow for price adjustments. The company’s dominant market position and the critical nature of its products provide significant pricing power 5 4. This enables GE Aerospace to largely pass on increased material and labor costs to customers, thereby protecting its profit margins even in an elevated inflationary environment.
Key Geopolitical & Macroeconomic Drivers Impacting GE Aerospace
| Driver Category | Specific Driver | Impact on GE Aerospace | Significance |
| Geopolitics | Russia-Ukraine Conflict | Increased Defense Spending | Long-term revenue stability for military segment |
| Geopolitics | US-China Strategic Competition | Sustained Demand for Advanced Military Tech | Predictable government contracts, R&D focus |
| Macroeconomics | Post-Pandemic Air Travel Rebound | Higher Flight Hours & Aftermarket Demand | High-margin revenue growth, service backlog |
| Macroeconomics | Fleet Modernization & Expansion | Increased New Engine Orders | Future revenue pipeline, market share capture |
| Macroeconomics | Inflationary Pressures | Managed Cost Increases via Pricing Power | Margin protection, financial resilience |
Navigating Trade Wars and Protectionism
A. US-China Trade Relations and Aviation
Trade tensions, particularly between the US and China, have created uncertainties and imposed tariffs on various goods. GE Aerospace mitigates these risks through its expansive global footprint and diversified manufacturing and supply chain operations. The company has established strategic partnerships and local presences in key regions worldwide. This diversification reduces its reliance on any single market or supply chain, lessening vulnerability to bilateral trade disputes. This proactive approach to global operations ensures supply stability and continued market access, even amidst shifting trade policies.
B. Export Controls and Technology Transfer
The US government has given the go-ahead for GE Aerospace to restart exporting aircraft engines to the Chinese manufacturer Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China (COMAC) 6 7. On July 3, 2025, restrictions previously put in place amid trade tensions with China were lifted 6 7. Towards the end of May 2025, the US suspended the export to COMAC of aircraft engines, plus other aviation-related technology. These included LEAP-1C engines and GE CF34 engines, which power the COMAC C919 and C909 respectively 7,. Both engines are made by CFM International, a joint venture between Safran and GE Aerospace 7. While export controls may limit some market opportunities, they reinforce GE Aerospace’s status as a trusted supplier to key strategic partners. This alignment can lead to preferential treatment and long-term contracts within critical defense sectors, solidifying its position in secure markets.
Innovation and Sustainable Aviation
A. Decarbonization and SAF Development
The aviation industry faces increasing pressure to decarbonize, driving significant investment in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF). GE Aerospace is at the forefront of this transition, investing heavily in the development of engines compatible with 100% SAF 8. The company also conducts extensive research into revolutionary propulsion technologies, including the RISE development program, demonstrating improved durability and fuel efficiency 5. Strategic partnerships with airlines, fuel producers, and research institutions accelerate the development and adoption of these sustainable solutions. Early and substantial investment in sustainable aviation technologies positions GE Aerospace as a leader in future propulsion systems. This not only addresses critical environmental concerns but also opens new market opportunities and strengthens relationships with airlines committed to achieving net-zero emissions.
B. Advanced Materials and Digital Technologies
Innovation in materials and digital technologies further enhances GE Aerospace’s competitive edge 5. Digital twin technology and predictive maintenance solutions are transforming engine MRO, allowing for real-time monitoring and proactive servicing. These technological advancements significantly improve engine performance, reduce operational costs for customers, and extend engine lifespan. Continuous innovation reinforces GE Aerospace’s market leadership and strengthens its high-margin aftermarket services business through enhanced efficiency and reliability.
Financial Performance and Outlook
A. Revenue and Profitability Trends
GE Aerospace’s financial performance post-spin-off demonstrates the benefits of its focused strategy. The company reported $1.49 earnings per share for the quarter, beating the consensus estimate of $1.29 by $0.20 9 10 5. It had revenue of $9.94 billion during the quarter, compared to analyst estimates of $9.06 billion 9 10 5. GE Aerospace had a return on equity of 29.15% and a net margin of 17.63% 9 5. The company has shown robust growth in both commercial engines and aftermarket services revenue, driven by the air travel recovery. The defense segment consistently contributes significant revenue, providing a stable base. Strategic initiatives aimed at operational efficiency and cost management are driving margin expansion across its businesses. The strong financial results validate the strategic rationale behind the spin-off, showcasing improved operational leverage and a more streamlined business model.
B. Cash Flow Generation and Capital Allocation
GE Aerospace generates strong free cash flow, reflecting its efficient operations and high-margin service business. This robust cash generation supports continued debt reduction, strengthening the company’s balance sheet. The financial flexibility allows for strategic capital allocation, including returns to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks. The company recently announced a quarterly dividend of $0.36 per share, payable on July 25th, representing a $1.44 annualized dividend and a 0.55% yield 9 11 12 13. GE Aerospace’s dividend payout ratio is currently 22.40% 9 13. Simultaneously, the company continues to invest substantially in research and development and other strategic growth initiatives to maintain its technological leadership. The strong cash flow provides the necessary resources for both long-term strategic investments and rewarding shareholders, signaling confidence in sustained performance.
C. Future Growth Catalysts
Several factors are poised to fuel GE Aerospace’s continued growth. Continued expansion in global air travel, particularly in emerging markets, will drive demand for new aircraft and engines. Ongoing defense modernization cycles across allied nations ensure a steady pipeline of military contracts. The company’s development of new engine programs and upgrades for existing fleets will capture future market share. Furthermore, GE Aerospace actively explores expansion into new aviation markets and applications, such as advanced air mobility. The convergence of commercial recovery, persistent defense demand, and a clear innovation roadmap creates multiple avenues for sustained growth, positioning GE Aerospace to capture significant value in a dynamic global aerospace landscape.
Conclusions and Outlook
GE Aerospace’s recent rise is a compelling narrative of strategic transformation intersecting with favorable global conditions. Its independence has sharpened focus, allowing the company to fully leverage its core strengths in propulsion and services. The confluence of escalating geopolitical tensions driving defense spending, a robust post-pandemic commercial aviation rebound, and a proactive approach to managing trade complexities has created a powerful tailwind. Furthermore, GE Aerospace’s commitment to innovation in sustainable aviation and advanced materials positions it for long-term leadership. The company demonstrates resilience and adaptability, effectively navigating global challenges while capitalizing on significant market opportunities. Its strong financial performance and clear growth catalysts suggest a sustained trajectory of market leadership in the global aerospace industry.
References
- ge-20221231 – SEC.gov, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/40545/000004054523000023/ge-20221231.htm
- GE SEC Filings: Current & Historic | General Electric, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.ge.com/investor-relations/sec-filings
- GE Aerospace Executives Sell Off Shares Amid Strategic Repositioning – AInvest, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.ainvest.com/news/ge-aerospace-executives-sell-shares-strategic-repositioning-2503/
- Mar Vista’s U.S. Quality Premier Strategy’s Q2 2025 Investor Letter – Insider Monkey, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.insidermonkey.com/blog/mar-vistas-u-s-quality-premier-strategys-q2-2025-investor-letter-1566756/
- GE Aerospace Announces First Quarter 2025 Results, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.geaerospace.com/news/press-releases/ge-aerospace-announces-first-quarter-2025-results
- US lets GE restart jet engine shipments to China’s COMAC, source says – IR Global, accessed July 15, 2025, https://irglobal.com/article/us-lets-ge-restart-jet-engine-shipments-to-chinas-comac-source-says/
- US allows GE Aerospace to resume engine shipments to China’s COMAC – Reuters, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.investing.com/news/stock-market-news/us-allows-ge-aerospace-to-resume-engine-shipments-to-chinas-comac–reuters-4123129
- China Airlines Signs Multi-Year Service Agreement with GE Aerospace for GE9X Engines, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.asdnews.com/news/aerospace/2025/07/07/china-airlines-signs-multiyear-service-agreement-with-ge-aerospace-ge9x-engines
- General Electric Co (GE) Stock Price & News – Google Finance, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.google.com/finance/quote/GE:NYSE
- www.geaerospace.com, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.geaerospace.com/news/press-releases/ge-aerospace-announces-first-quarter-2025-results#:~:text=Total%20orders%20of%20%2412.3B,*%20%242.1B%2C%20%2B38%25
- GE Aerospace Board of Directors Authorizes Regular Quarterly Dividend – Nasdaq, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.nasdaq.com/press-release/ge-aerospace-board-directors-authorizes-regular-quarterly-dividend-2025-06-27
- GE Aerospace Declares Regular Quarterly Dividend, Payable July 25, 2025 – Finnhub, accessed July 15, 2025, https://finnhub.io/api/news?id=de304295a4c756f3d1cc7a517ecbcc4382bb8fca37f7164091edd10936a1c24a
- Mohamed Ali Sells 1,602 Shares of GE Aerospace (NYSE:GE) Stock – MarketBeat, accessed July 15, 2025, https://www.marketbeat.com/instant-alerts/ge-aerospace-nysege-svp-sells-32147334-in-stock-2025-05-01/
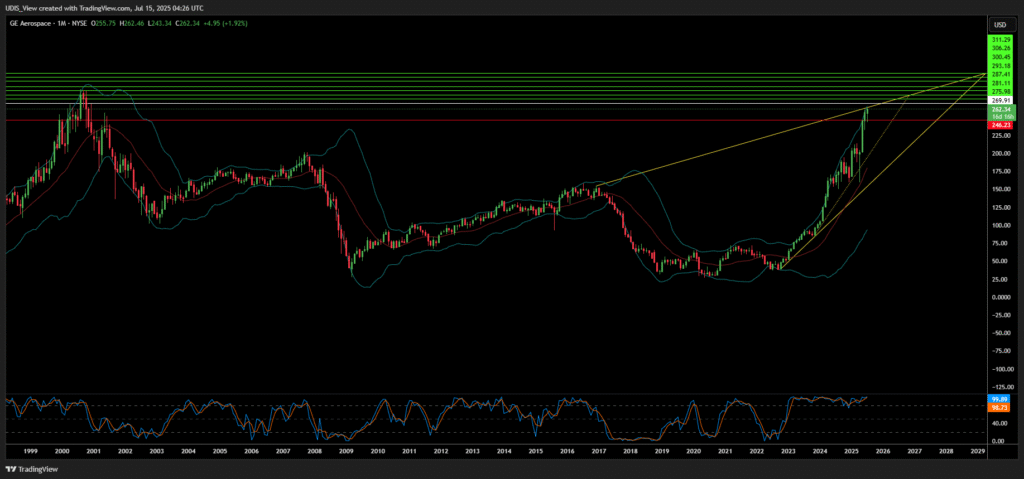
GE Aerospace Long (Buy)
Enter At: 269.91
T.P_1: 275.98
T.P_2: 281.11
T.P_3: 287.41
T.P_4: 293.18
T.P_5: 300.45
T.P_6: 306.26
T.P_7: 311.29
S.L: 246.23