The Convergence of Capital, Geostrategy, and Innovation
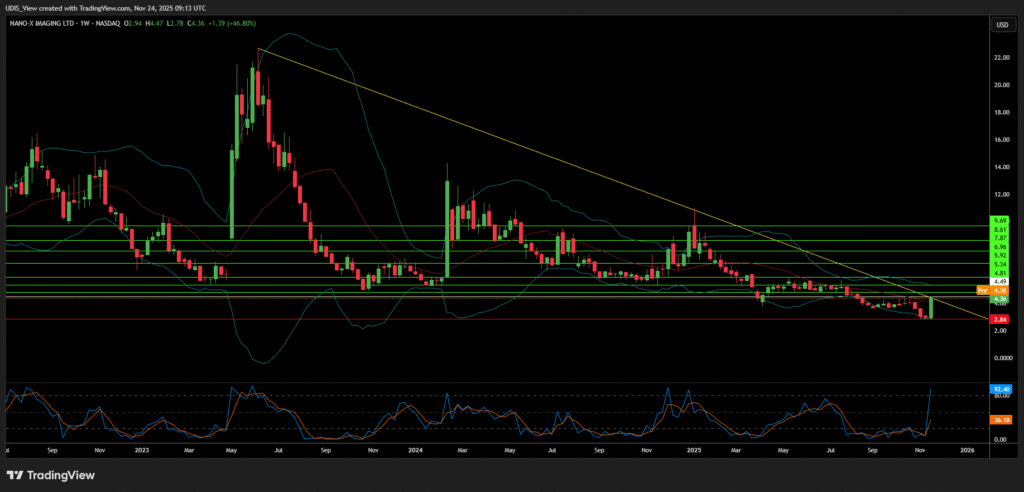
The trajectory of Nano-X Imaging (NASDAQ: NNOX) has shifted decisively from speculative development to commercial execution, marked by a confluence of strategic milestones in late 2025. This report provides an exhaustive analysis of the company’s operational status, financial outlook, and technological positioning as it pivots toward a projected $35 million revenue target for fiscal year 2026.1
The central thesis of this analysis posits that Nano-X is not merely an equipment manufacturer but the architect of a structural shift in the economics of medical imaging.
This shift is driven by three interconnected vectors:
- Technological Disruption: The successful industrialization of the cold cathode X-ray source, validated by the operational status of the semiconductor fabrication plant in South Korea.3
- Business Model Innovation: The “Medical Screening as a Service” (MSaaS) model, which aligns perfectly with a high-interest-rate macroeconomic environment that disincentivizes traditional heavy capital expenditure (CapEx) by hospitals.5
- Geopolitical Resilience: A deliberate decentralization of the supply chain, moving critical component manufacturing to the SK Hynix cluster in South Korea, thereby insulating the company’s core value creation from regional instability in the Middle East.7
Recent developments, including the $15 million registered direct offering 9 and the landmark partnership with 3DR Labs 10, provide the necessary liquidity and distribution channels to execute this vision.
With a robust pipeline targeting $72.6 million in revenue by 2028 1, Nano-X presents a compelling case for asymmetric upside, trading at a valuation that arguably lags the de-risking events of the past twelve months.
1. Technological Sovereignty: The Physics of the Cold Cathode Revolution
1.1 The Century-Old Bottleneck: Thermionic Emission
To understand the magnitude of Nano-X’s innovation, one must first appreciate the stagnation of the incumbent technology.
For over 125 years, medical imaging has relied on the principles established by Wilhelm Röntgen and refined by William Coolidge in 1913.11 The standard X-ray tube operates via thermionic emission: a tungsten filament is heated to temperatures exceeding 2,000°C to “boil off” electrons, which are then accelerated toward an anode to produce X-rays.11
This process is fundamentally inefficient. Approximately 99% of the electrical energy input is converted into waste heat rather than X-ray photons.11 This thermodynamic reality imposes severe physical constraints on system design.
Traditional CT scanners require massive, oil-filled cooling housings and rotating gantries to dissipate heat and distribute the electron beam’s impact. These engineering requirements dictate the high cost, large footprint, and immobility of legacy systems (GE, Siemens, Philips), effectively tethering high-quality imaging to hospital basements 13
1.2 The Nanox.SOURCE: Field Emission and MEMS Integration
Nano-X has commercialized a cold cathode system that utilizes field emission rather than thermionic emission.
The Nanox.SOURCE is a semiconductor chip containing millions of molybdenum nano-cones.12 When a specific voltage is applied, electrons are extracted from these cones via quantum tunneling, a process that occurs at room temperature.13
Technological Superiority:
- Thermal Efficiency: By eliminating the need to heat a filament, the Nanox.SOURCE removes the primary source of waste heat. This allows for a drastic reduction in the size and weight of the tube, as complex cooling systems are rendered obsolete.12
- Digital Agility: Unlike a hot filament, which has a thermal lag (time to heat up and cool down), the Nanox cold cathode can be toggled on and off instantaneously.15 This rapid switching capability is the cornerstone of the Nanox.ARC’s design enables it to pulse X-rays from multiple stationary sources in sequence, capturing tomosynthesis images without the mechanical vibration and complexity of a rotating gantry.16
- MEMS Scalability: The production of the source utilizes Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology. This shifts the manufacturing paradigm from the artisanal assembly of vacuum tubes to the mass production of silicon wafers.4
1.3 The Manufacturing Moat: South Korean Fabrication
A critical differentiator for Nano-X is its vertical integration. Unlike competitors that may rely on third-party suppliers for novel components, Nano-X has established its own semiconductor fabrication plant in Yongin, South Korea.3
Facility Specifications and Capabilities:
- Scale: The facility spans 12,000 square meters, including a 1,200-square-meter MEMS clean room.4
- Advanced Processes: The plant is equipped for 200nm photolithography using krypton fluoride (KrF) scanners, electrochemical metal etching, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).17 These are advanced semiconductor manufacturing processes that ensure high yield and consistency of the nano-cone structures.
- Strategic Location: Situated next to the world’s largest semiconductor cluster (SK Hynix), the facility benefits from a rich ecosystem of talent, raw material suppliers, and logistics infrastructure.8 This proximity allows Nanox to leverage the “silicon shield” of South Korea’s industrial base.
2. The Commercial Engine: Partnerships and Distribution Channels
2.1 The 3DR Labs Catalyst: Immediate Scale
The partnership with 3DR Labs, announced in November 2025, represents the most significant commercial validation of the Nanox ecosystem to date. 3DR Labs is not merely a reseller; it is a premier provider of medical image post-processing, serving a network of over 1,800 hospitals and diagnostic centers across the United States 19
Strategic Synergies:
- Market Penetration: This agreement grants Nanox immediate access to an established customer base. Rather than building a sales force to knock on 1,800 hospital doors, Nanox leverages 3DR Labs’ existing trusted relationships.10
- Workflow Integration: 3DR Labs employs over 300 expert radiologic technologists who provide 24/7 image processing.10 By integrating Nanox.AI algorithms (HealthCCSng, HealthOST, HealthFLD) into 3DR Labs’ workflow, the adoption friction is effectively zero. The AI findings are delivered as part of the standard report, enhancing the value proposition for the hospital without requiring them to install new software or train staff.20
- Revenue Layering: This partnership supports the 2026 revenue guidance by adding a high-margin software revenue stream that is independent of hardware installation velocity.
2.2 VasoHealthcare IT: The Integration Bridge
Complementing the 3DR Labs deal is the acquisition of VasoHealthcare IT.21 As a wholly-owned subsidiary of Vaso Corporation, VasoHealthcare IT specializes in the “last mile” of medical IT integrating disparate systems into hospital Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Electronic Health Records (EHR).21
This acquisition solves a critical implementation bottleneck. While 3DR Labs provides the distribution and processing, VasoHealthcare IT ensures that the data flows seamlessly from the Nanox.ARC or the AI cloud into the hospital’s central nervous system. This capability is essential for large-scale enterprise deployments where IT interoperability is a strict requirement.21
2.3 International Expansion Vectors
While the US remains the primary revenue focus, Nanox is aggressively cultivating international markets to prove the global viability of the MSaaS model.
- France: The deployment of the Nanox.ARC at Hospital Privé Jacques Cartier in Massy, near Paris, serves as a critical European reference site.23 Partnering with Olympe Imagerie, this site is conducting clinical trials for lung cancer detection, a high-value application that demonstrates the system’s clinical utility beyond basic bone imaging.23
- Mexico: The agreement with SPI Medical to deploy 630 Nanox.ARC units represent a massive commitment to the Latin American market.24 This deal highlights the appeal of the MSaaS model in emerging economies where capital constraints often prevent the acquisition of high-end imaging modalities.
- Ghana: Deployments in Ghana illustrate the humanitarian and “access-to-care” dimension of the Nanox mission, bringing diagnostic capabilities to regions with severe infrastructure deficits.1
- South Korea & Vietnam: Supported by SK Telecom, Nanox plans to deploy 2,500 systems across these two nations.25 SK Telecom’s role extends beyond investment; they are facilitating the regulatory and logistical groundwork to make these deployments a reality, leveraging their 5G expertise to handle the data transmission requirements.25
2.4 Monarch Medical: Niche Market Dominance
In the US, the subsidiary Nanox Impact Inc. has collaborated with Monarch Medical Management to target specific healthcare niches: workers’ compensation, nursing homes, and outpatient clinics.27
- Strategic Rationale: These facilities often lack on-site imaging, forcing patients to be transported to hospitals for basic scans. This is costly and inefficient. Placing a Nanox.ARC on-site (enabled by its small footprint and low cost) creates immediate ROI by capturing revenue that would otherwise be lost to third-party imaging centers.27
- Workers’ Comp: Rapid imaging in workers’ compensation cases speeds up diagnosis and claim processing, a critical KPI for insurance payers in this sector.
3. Financial Architecture: Modeling the Pivot
3.1 The $35 Million Revenue Guidance (2026)
Management’s issuance of a $35 million revenue outlook for 2026 is a watershed moment, representing a massive inflection from the $3.45 million reported in Q3 2025.1
Deconstructing the Forecast:
The bridge to $35 million is built on three pillars:
- Hardware Revenue Recognition: As deployments in the US (3DR Labs network) and Mexico (SPI) come online, revenue from hardware placement fees (where applicable) and initial service setup will surge.
- SaaS/AI Licensing: The recurring revenue from the 3DR Labs deal for AI algorithms (HealthCCSng, HealthOST) creates a high-margin base.20
- Scan Volume Ramp: As the installed base grows, the “per-scan” revenue will begin to compound. Early data from active sites in California indicate “above-average scanning levels” and positive feedback, validating the utilization assumptions underlying the guidance.21
3.2 The $15 Million Capital Injection
The $15 million registered direct offering executed in November 2025 provides the working capital runway necessary to support this manufacturing ramp.9
- Use of Proceeds: The funds are explicitly earmarked for “working capital and corporate uses,” which effectively translates to inventory buildup (Nanox.ARC units) and sales/marketing expenses associated with the US expansion.28
- Balance Sheet Strength: As of September 30, 2025, Nanox held $55.5 million in cash and equivalents.29 While this is a decrease from $83.2 million at the end of 2024, the $15 million raise stabilizes the liquidity position, bridging the gap to cash flow positivity expected in later years.
- Burn Rate Management: With a negative operating cash flow of $30.4 million in the reported period 29, the company is under pressure to execute. However, the pivot to revenue generation in 2026 is designed to dramatically narrow this burn.
3.3 Analyst Valuation and Sentiment
The market has responded positively to the clarity of the 2026 guidance. Analyst consensus rates the stock a “Strong Buy,” with price targets averaging $7.75 representing a potential upside of over 120% from the $3.50 trading range.1 More aggressive targets, such as the $23 price target from D. Boral Capital 32, suggest that if Nanox successfully executes the MSaaS model at scale, the valuation multiple could expand significantly to match high-growth SaaS or MedTech peers.
4. Macroeconomic and Geopolitical Tailwinds
4.1 The CapEx vs. OpEx Dynamic in 2025
The healthcare capital equipment market is facing headwinds from elevated interest rates and inflationary pressures on hospital budgets.5 In this environment, hospital CFOs are reluctant to approve multi-million dollar capital expenditures (CapEx) for new CT scanners or MRI machines.
The Nanox Advantage:
- MSaaS: The model converts imaging costs from CapEx to OpEx.6
- Financial Flexibility: Hospitals pay for the scans they use, aligning expenses directly with revenue. This removes the risk of underutilization and preserves precious capital for other needs 35
- Tariff Immunity: While competitors face rising costs due to tariffs on imported medical equipment components 5, Nanox’s service-based model shields the end customer from hardware price fluctuations. The hospital buys the service, not the machine.
4.2 Israel’s Tech Sector Resilience
Despite the “Iron Swords” war and regional instability, Israel’s high-tech sector has demonstrated remarkable resilience. 2025 has seen a recovery in fundraising and record exits, reinforcing the view that Israeli tech is “antifragile”.7 Nanox, headquartered in Neve Ilan, benefits from this ecosystem of innovation while actively hedging its operational risks.
4.3 Supply Chain Geostrategy
Nanox has executed a textbook geopolitical hedge by decoupling its R&D headquarters (Israel) from its manufacturing hub (South Korea).
- Risk Mitigation: By placing the semiconductor fabrication in the SK Hynix cluster, Nanox ensures that a conflict in the Middle East will not sever the supply of its most critical component.3
- Global Logistics: South Korea serves as an ideal logistics hub for Asian and global distribution, bypassing potential bottlenecks in the Mediterranean or Red Sea.
5. Regulatory, Compliance, and Cyber Sovereignty
5.1 The FDA Shield
The most potent rebuttal to historical short-seller critiques (e.g., Muddy Waters, Citron) is the FDA 510(k) clearance of the Nanox.ARC.1 Regulatory clearance is not merely a stamp of approval; it is a validation of the physics. The FDA does not clear “fake” technology. This milestone fundamentally de-risks the technology aspect of the investment thesis.38
5.2 Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
As a cloud-native medical device (IoMT), Nanox operates at the intersection of healthcare and cybersecurity. The Nanox.CLOUD architecture is built to withstand the rigorous demands of global data privacy laws.
- Certifications: Nanox maintains compliance with ISO 27001 (Information Security Management) and ISO 27799 (Health Informatics).39 In the US, the system is HIPAA compliant, and in Europe, it adheres to GDPR/UK GDPR standards 39
- Local Sovereignty: To operate in France, Nanox adheres to specific certifications for hosts of health data.39 In Israel, cloud systems for the public health sector require specific ISO certifications, which Nanox has secured.
- HITRUST Alignment: The company’s security posture aligns with the HITRUST CSF framework, which harmonizes HIPAA, ISO, and NIST standards into a single, rigorous control set.40 This is a critical requirement for selling into large US health systems.
6. Competitive Landscape: Defining the Niche
6.1 Cold Cathode Rivals: Micro-X and Varex
Nanox is not alone in the pursuit of cold cathode technology, but its business model sets it apart.
- Micro-X (Australia): Uses carbon nanotube (CNT) emitters and has partnered with Varex Imaging (a major tube manufacturer) and Carestream for mobile DR systems.13
- Differentiation: Micro-X and Varex primarily operate on a traditional hardware sales model, selling better tubes to existing OEMs. Nanox, conversely, is building an end-to-end ecosystem. Nanox does not want to sell the tube to GE; they want to replace the GE machine with a service that renders the ownership of the machine irrelevant.14
6.2 The Tomosynthesis Advantage
Most cold cathode competitors are focused on mobile 2D X-ray (digital radiography). Nanox.ARC is a digital tomosynthesis system (3D imaging).1 This places it in a different clinical category—capable of providing depth resolution that a standard X-ray cannot, at a fraction of the radiation and cost of a full CT scan. This “in-between” modality is ideal for the screening applications (lung, bone, cardiac) that Nanox targets.
7. Strategic Outlook and Conclusion
7.1 The Path to $72.6 Million
The bridge from 2026 ($35M) to 2028 ($72.6M) relies on the network effect of the installed base. As more units are deployed, the teleradiology marketplace liquidity improves, AI algorithms become more refined on larger datasets, and the recurring revenue creates a flywheel effect.1
7.2 Key Risks and Mitigations
- Adoption Rate: The primary risk is the speed at which hospitals embrace the MSaaS model. The 3DR Labs partnership mitigates this by layering value (AI) onto existing workflows immediately.
- Regulatory Expansion: Delays in obtaining regulatory clearance in new markets (e.g., South Korea, Vietnam) could slow the deployment timeline. The partnership with SK Telecom is a direct mitigation strategy here, leveraging local influence to navigate bureaucracy.
- Capital Needs: While the $15M raise helps, the burn rate remains high. Continued execution is required to prevent further dilutive raises before cash flow breakeven is achieved.
7.3 Final Assessment
Nano-X Imaging has successfully navigated the “Valley of Death” between prototype and product. The operational reality of the South Korean factory, the FDA clearances, and the commercial contracts with 3DR Labs and SPI Medical serve as tangible proofs of execution.
The company is capitalizing on a “perfect storm” of industry trends:
- Macro: High rates favor OpEx (MSaaS) over CapEx.
- Clinical: Radiologist shortages demand AI and teleradiology solutions.
- Strategic: Supply chain decentralization ensures continuity.
For professional observers, NNOX represents a unique case study in deep-tech commercialization. By fundamentally restructuring the economic relationship between the medical device vendor and the healthcare provider, Nano-X is positioning itself to capture significant value in the transition to decentralized, preventive healthcare. The $35 million revenue target for 2026 is the first major financial validation of this disruptive potential.
Nanox Long (Buy)
Enter At: 4.49
T.P_1: 4.81
T.P_2: 5.34
T.P_3: 5.92
T.P_4: 6.96
T.P_5: 7.87
T.P_6: 8.61
T.P_7: 9.69
S.L: 2.84