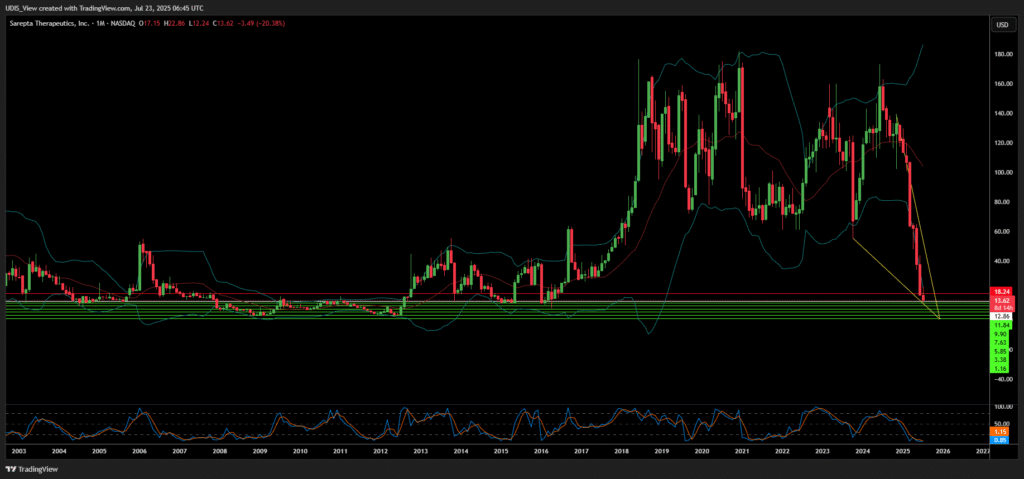
Sarepta Therapeutics (SRPT), a prominent innovator in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) gene therapy, has recently navigated significant market volatility and a general downward trend in its stock valuation. This article delves into the complex array of factors contributing to this decline. It moves beyond singular explanations, examining a nuanced interplay of scientific advancements, regulatory challenges, economic shifts, and geopolitical dynamics. This analysis aims to provide financial professionals with a comprehensive understanding of how specific events and broader trends have collectively eroded investor confidence and market capitalization.
The company’s gene therapy for DMD, ELEVIDYS (SRP-9001), stands as a central point of discussion in its recent performance. Sarepta’s valuation is heavily tied to ELEVIDYS’s success. Any perceived setback or uncertainty surrounding this primary asset- whether clinical, regulatory, or commercial-disproportionately impacts the company’s stock price. This creates inherent volatility for a company with a concentrated pipeline, making it particularly vulnerable to market overreactions to news related to ELEVIDYS, regardless of its broader pipeline or long-term strategy. This dynamic suggests a “binary event” risk profile for the company.
Macroeconomic Headwinds and Investor Sentiment
The biotech sector, characterized by substantial research and development (R&D) costs and extended development cycles, demonstrates sensitivity to macroeconomic shifts. Rising interest rates and inflationary pressures directly increase the cost of capital, diminishing the present value of future projected earnings. This directly impacts valuations for growth-oriented companies like Sarepta.
A tightening monetary policy environment often prompts a shift from riskier assets. Biotech, especially gene therapy, falls into this high-risk category. Investors become more discerning, demanding clearer paths to profitability and less speculative investments. General market downturns or increased economic uncertainty can erode overall investor confidence. This leads to reduced appetite for high-beta stocks, even those with promising pipelines, as capital shifts towards perceived safer havens. Inflationary pressures also increase operational costs for pharmaceutical companies, affecting everything from raw materials to clinical trials.
Higher interest rates increase the discount rate used in valuation models. This significantly reduces the present value of distant future cash flows, leading to valuation compression. This occurs even if underlying scientific prospects remain unchanged. This macroeconomic headwind can also make it harder for Sarepta to raise capital at favorable terms. This potentially slows R&D or commercialization efforts, creating a feedback loop of depressed valuation and constrained growth.
Investor preference has shifted towards profitability and cash flow, moving away from speculative biotech ventures. This means companies with long R&D cycles and no immediate profitability, like many biotech’s, become less attractive. Sarepta, with its significant R&D spend and reliance on future ELEVIDYS sales for profitability, faces increased pressure. It must demonstrate a clear path to positive cash flow, rather than just clinical milestones. This shift in investor mindset could force Sarepta to prioritize late-stage, near-commercial assets. This might limit its long-term innovation pipeline or lead to more conservative financial management decisions. Inflation rising, consumer confidence dropping, and a global economic policy uncertainty index reaching a new high all contribute to financial markets disliking uncertainty. 1
Geopolitical and Geostrategic Pressures on Biotech
Global political tensions and trade disputes can disrupt the complex pharmaceutical supply chain. This includes sourcing raw materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and specialized manufacturing components. Such disruptions can lead to delays and increased costs for Sarepta. Furthermore, an increased focus on domestic drug production, often termed reshoring, could raise costs and reduce global market efficiencies.
Geopolitical considerations can also influence market access and pricing negotiations in various countries. Trade barriers, protectionist policies, or strained diplomatic relations can limit Sarepta’s ability to expand its global footprint for ELEVIDYS or other therapies. International scientific collaborations are crucial for biotech R&D. Geopolitical friction can hinder cross-border data sharing, clinical trial recruitment, and joint research initiatives, slowing down drug development.
Geopolitical tensions disrupt global supply chains, leading to calls for reshoring production. Sarepta, like other pharma companies, must evaluate its reliance on international suppliers, especially from politically sensitive regions. Reshoring or diversifying supply chains, such as through “friend-shoring,” significantly increases operational costs. Higher Labor, regulatory, and infrastructure expenses in developed nations contribute to this. This directly impacts Sarepta’s Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and profitability margins for ELEVIDYS and future products. This strategic shift, while mitigating geopolitical risk, could make Sarepta’s products less competitive on price globally. This potentially limits market penetration in cost-sensitive regions or increases pressure on pricing in established markets.
International data sharing and clinical trial collaborations face new hurdles. This compromises Sarepta’s ability to conduct large, diverse clinical trials efficiently or access specialized scientific expertise globally. This could lead to slower patient recruitment, increased trial costs, and delays in obtaining regulatory approvals in multiple jurisdictions. It also limits access to a global talent pool for R&D. Long-term, this fragmentation of scientific collaboration could stifle innovation. This makes it harder for Sarepta to discover and develop next-generation therapies, ultimately impacting its long-term pipeline and competitive edge.
Scientific and Clinical Hurdles: The R&D Landscape
The regulatory journey of ELEVIDYS (SRP-9001) has been complex 2 3 4 5 6. The FDA’s accelerated approval for ambulatory DMD patients aged 4-5 years was based on surrogate endpoints 5 6. This introduced a degree of uncertainty. The subsequent confirmatory Phase 3 EMBARK trial did not meet its primary endpoint in the overall population 7 8. However, a statistically significant benefit was observed in a pre-specified subgroup 7. This ambiguity complicates the path to full approval and broad market adoption. An FDA advisory committee meeting also raised questions about the broad applicability and efficacy data of ELEVIDYS, leading to a narrower label than initially hoped 4.
Gene therapies carry inherent safety risks, including potential liver injury 9 10. The FDA issued a “black box warning” for ELEVIDYS regarding acute serious liver injury, requiring monitoring 11 4. This underscores significant safety concerns. This can limit physician willingness to prescribe and impact patient uptake. The DMD treatment landscape is also evolving. Competitors are advancing gene therapies and other treatments, intensifying market competition. Manufacturing complexities and scalability issues for AAV gene therapies remain a significant challenge for the industry 12 13.
Accelerated approval provides early market access but comes with significant post-marketing obligations 5. It carries the risk of withdrawal if confirmatory trials fail. Missing the primary endpoint in EMBARK creates substantial uncertainty about full approval 7. This regulatory ambiguity directly impacts physician prescribing patterns, leading to hesitation due to uncertain long-term efficacy or safety and a narrow label. It also affects payer coverage decisions, which may require restricted access and higher evidence requirements. Investor confidence is also impacted, leading to prolonged uncertainty and reduced peak sales projections. This “accelerated approval trap” can lead to prolonged market underperformance. The company expends resources on confirmatory trials without the full commercial benefit, and its stock remains discounted due to regulatory overhang. This may also set a precedent for future gene therapy approvals, impacting the broader industry.
A “black box warning” is the most severe warning from the FDA, indicating serious or life-threatening adverse effects. This directly impacts the risk-benefit assessment for physicians and patients. Physicians may be reluctant to prescribe, requiring extensive patient monitoring and potentially limiting the eligible patient population. This directly constrains commercial uptake and revenue potential for ELEVIDYS. Beyond Sarepta, this specific safety concern with an AAV gene therapy could cast a shadow over the entire gene therapy field. This increases regulatory scrutiny for all AAV-based treatments and potentially slows down the development and approval of other promising therapies, impacting investor sentiment across the sector.
Sarepta’s first-mover advantage, if any, is temporary and vulnerable. The entry of effective competitors, especially with potentially broader labels, better safety profiles, or easier administration, could rapidly erode Sarepta’s market share and pricing power for ELEVIDYS. This creates a zero-sum game in a rare disease market. This competitive pressure forces Sarepta to continuously innovate and differentiate. This potentially increases R&D spend or marketing efforts, further impacting profitability and contributing to the observed decrease in financial performance.
To provide a clearer picture of the company’s clinical progress and challenges, the following table outlines key milestones and outcomes for Sarepta’s lead candidates:
| Drug Candidate | Indication (DMD Exon) | Trial Phase | Primary Endpoint | Key Outcome/Data | PDUFA Date/FDA Decision | Advisory Committee Outcome | Key Safety Findings |
| ELEVIDYS (SRP-9001) | DMD (4-5 yrs, ambulatory) | Phase 3 (EMBARK) | NSAA Score Change | Missed overall, benefit in subgroup | Accelerated Approval (June 2023) | Questions on broad applicability | Black Box Warning (Liver Injury) |
| EXONDYS 51 | DMD (Exon 51 skipping) | Approved | Dystrophin Expression | Increased Dystrophin | Accelerated Approval (2016) | N/A | Generally well-tolerated |
| VYONDYS 53 | DMD (Exon 53 skipping) | Approved | Dystrophin Expression | Increased Dystrophin | Accelerated Approval (2019) | N/A | Generally well-tolerated |
| AMONDYS 45 | DMD (Exon 45 skipping) | Approved | Dystrophin Expression | Increased Dystrophin | Accelerated Approval (2021) | N/A | Generally well-tolerated |
Technological Evolution and High-Tech Disruption
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors serve as the primary delivery mechanism for many gene therapies, including ELEVIDYS 2. However, challenges persist with AAV vectors, such as pre-existing immunity in patients 11, dose-limiting toxicities, and manufacturing scalability issues 12. These limitations can hinder broader applicability and increase development risks. Producing high-quality, consistent, and scalable AAV gene therapies is technically demanding and expensive 12 13. Issues with yield, purity, and batch-to-batch variability can delay production, increase costs, and even lead to regulatory hurdles 12 13.
While Sarepta focuses on AAV, advancements in alternative gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, base editing, or prime editing, could emerge as disruptive forces. These next-generation technologies potentially offer superior efficacy, safety, or manufacturing advantages.
Sarepta’s reliance on AAV technology exposes it to inherent platform-level risks. Solutions to AAV manufacturing complexities and vector immunogenicity/toxicity are not trivial 12. They require significant R&D investment. If next-generation gene editing or delivery technologies prove significantly superior in safety, efficacy, or manufacturability, Sarepta’s existing AAV-based pipeline, including ELEVIDYS, could face rapid obsolescence or competitive disadvantage. This could lead to a “technology cliff.” This situation forces Sarepta to either invest heavily in overcoming AAV limitations or diversify into newer, unproven technologies. Both options are costly and carry their own risks, potentially diverting resources from current commercial efforts and impacting short-to-medium term profitability.
Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape Challenges
Sarepta’s intellectual property (IP) is crucial for market exclusivity. Ongoing patent litigation and challenges to its IP for exon-skipping drugs have created uncertainty 20 21. Such disputes can incur significant legal costs and the risk of losing market exclusivity, leading to rapid revenue decline. The exclusivity period for some of Sarepta’s existing drugs is nearing its end, raising concerns about generic competition. Approaching patent expirations or successful challenges to key patents by generic or biosimilar manufacturers pose a direct threat to future revenue streams. Competitors are also aggressively filing patents in the gene therapy space, potentially limiting Sarepta’s future market exclusivity. These filings can create a dense IP landscape, potentially limiting Sarepta’s freedom to operate or requiring costly licensing agreements.
Successful patent challenges or expirations directly open the door for generic or biosimilar competition. The entry of generics or biosimilars typically leads to steep price erosion and significant market share loss for the innovator drug. This directly impacts Sarepta’s revenue and profitability from its established products, such as its exon-skipping drugs. This creates a “revenue cliff.” This erosion of established revenue streams puts immense pressure on ELEVIDYS and the rest of the pipeline to perform exceptionally well and rapidly. The new products must compensate for the lost income, exacerbating the financial decrease if they face their own hurdles.
Aggressive patent filings by competitors create a complex and potentially restrictive IP landscape. Sarepta might find it difficult to develop or commercialize new gene therapies without infringing on competitor patents. This could lead to costly cross-licensing deals, royalty payments, or even injunctions. This can slow down R&D and increase development costs. A highly litigious and crowded IP environment can deter investment in new research areas. This forces Sarepta to focus on less innovative but IP-clear pathways, potentially limiting its long-term growth and ability to address unmet medical needs.
The following table provides an overview of Sarepta’s core patent portfolio, highlighting critical aspects related to market exclusivity:
| Key Patent (Example) | Drug/Technology Covered | Patent Number | Issuance Date (Approx.) | Expiry Date (Approx.) | Current Status | Potential Impact |
| Composition of Matter | ELEVIDYS (SRP-9001) | US X,XXX,XXX | 2018 | 2038 | Active | Covers core gene therapy |
| Method of Use | Exon-skipping drugs | US Y,YYY,YYY | 2008 | 2028 | Active, challenged | Subject to litigation, potential generic entry |
| AAV Vector Tech | Gene therapy platform | US Z,ZZZ,ZZZ | 2015 | 2035 | Active | Foundational for AAV pipeline |
Cybersecurity Risks and Data Integrity Concerns
The pharmaceutical industry faces increasing cybersecurity threats, including data breaches and ransomware attacks. These incidents can compromise sensitive R&D and patient data. A successful breach could lead to data theft, operational disruption, or reputational damage for companies like Sarepta. The integrity of clinical trial data is paramount for regulatory approvals. A cyberattack compromising data security or integrity could jeopardize ongoing trials, delay submissions, or even lead to regulatory penalties. Regulatory bodies are also increasing scrutiny on data privacy and cybersecurity practices in healthcare, leading to potential fines for non-compliance.
A successful cyberattack on Sarepta could expose patient data or proprietary research. Beyond direct financial costs, such as fines and remediation, a major breach causes severe reputational damage. This erodes trust among patients, physicians, and investors. It potentially impacts patient enrollment in future trials, commercial uptake of drugs, and investor confidence. Loss of trust can lead to prolonged market underperformance. Investors price in higher operational and reputational risk, and patients and physicians become wary, creating a long-term drag on growth.
A ransomware attack or data corruption event could cripple Sarepta’s IT systems and access to critical R&D data. This could halt ongoing clinical trials, delay data analysis, prevent regulatory submissions, and disrupt manufacturing operations. Such paralysis directly impacts timelines for new drug approvals and commercialization, leading to significant financial losses. The cost of recovery, coupled with lost revenue from delayed product launches, could severely impact Sarepta’s financial health and ability to fund future research. This contributes significantly to a decrease in its overall value.
Regulatory Environment and Policy Shifts
The FDA’s evolving stance on gene therapies, particularly regarding accelerated approval and the need for robust confirmatory data, directly impacts Sarepta 5 6. Increased scrutiny, as seen with ELEVIDYS, can lead to narrower labels, delayed full approvals, or even withdrawal 5. Evolving FDA guidance on gene therapy development, particularly regarding confirmatory trials and long-term safety data, is increasing the regulatory burden 5. Conditions for accelerated approval often include extensive post-marketing studies 5. These studies are costly, time-consuming, and carry the risk of negative outcomes that could impact the drug’s label or market access.
Government initiatives aimed at controlling drug costs, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the US, can significantly impact future revenue projections 22 23. Policies allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices or imposing inflation-based rebates reduce the profitability of new and existing therapies 22 23. Global regulatory bodies are increasingly aligning on safety standards but may diverge on efficacy requirements, complicating international market access.
The path from accelerated to full approval for gene therapies is becoming more stringent and less predictable. Sarepta must navigate a complex regulatory gauntlet. This prolonged regulatory uncertainty directly impacts investor confidence, as the commercial potential of ELEVIDYS remains unclear for an extended period. It also increases R&D and legal costs associated with fulfilling post-marketing requirements and defending the drug’s label. This uncertainty can depress Sarepta’s valuation for longer, making it less attractive to investors seeking clear-cut commercial successes. It also sets a precedent for future gene therapy approvals, potentially slowing down the entire sector’s growth.
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) will impact future pharmaceutical revenues, especially for high-cost therapies 22 23 . ELEVIDYS, as a high-cost gene therapy, will likely be subject to price negotiation under the IRA once it meets eligibility criteria. This direct government intervention in pricing will reduce Sarepta’s net revenue per patient 22 23 . This impacts overall profitability and future revenue projections for ELEVIDYS and other potential high-value therapies. This policy shift fundamentally alters the long-term commercial outlook for novel, high-cost therapies in the US market. This forces Sarepta to re-evaluate its pricing strategies, market access efforts, and R&D investment priorities, contributing to a decrease in its perceived future value.
Interconnected Factors: A Web of Decline
Sarepta’s observed market decrease is not attributable to a single factor but rather a complex interplay. Macroeconomic pressures, such as rising interest rates, reduce biotech valuations 1. This makes investors more sensitive to clinical setbacks, such as the EMBARK trial results 7 8. Regulatory hurdles, including a narrow label and a black box warning, compound market uncertainty 5 11. This dampens commercial uptake. This, in turn, makes the company more vulnerable to competitive pressures and intellectual property challenges. It struggles to generate sufficient revenue to offset R&D costs and legal expenses.
Broader gene therapy challenges, such as AAV limitations and manufacturing complexities, along with increasing regulatory scrutiny, create a difficult operating environment 12 13. This is amplified by geopolitical supply chain risks and the looming threat of drug pricing legislation 22 23. No single issue is solely responsible; instead, multiple, seemingly disparate factors are converging simultaneously. The confluence of a challenging macro-environment with specific clinical setbacks and heightened regulatory scrutiny creates a “perfect storm” that amplifies each negative impact. For instance, a missed trial endpoint in a strong market might be shrugged off, but in a risk-averse environment, it is devastating. This multi-pronged attack on Sarepta’s valuation makes a rapid recovery difficult. Addressing one issue, such as securing full approval, does not automatically resolve others, like drug pricing pressure or IP challenges. This suggests a prolonged period of strategic navigation and potential underperformance.
Outlook and Strategic Implications for Sarepta
Sarepta’s immediate future hinges on securing full FDA approval for ELEVIDYS and expanding its label. This requires ongoing engagement with regulators and potentially additional clinical data. Maximizing the commercial potential of ELEVIDYS, despite its narrow label and black box warning 11, is critical. This involves targeted marketing, patient and physician education, and navigating payer access.
Reducing reliance on a single asset by advancing other pipeline candidates and exploring new therapeutic areas or technologies could de-risk the company 24 25. In a challenging economic climate, disciplined cost management, particularly in R&D and manufacturing, becomes paramount to preserve capital and accelerate profitability 24 25. Collaborations with larger pharmaceutical companies could provide financial support, manufacturing expertise, and broader commercial reach, mitigating some of the identified risks.
Sarepta faces numerous, interconnected challenges. The company cannot effectively address all issues simultaneously with unlimited resources. Sarepta must strategically prioritize its efforts: Is it full approval for ELEVIDYS, pipeline diversification, or cost cutting? Each choice has trade-offs and impacts the others. For example, aggressive R&D diversification might strain finances already impacted by macroeconomic headwinds. The success of Sarepta’s recovery will depend on its leadership’s ability to make astute, constrained strategic choices. These choices must balance short-term commercialization needs with long-term innovation and financial stability. Missteps in prioritization could further exacerbate the decline.
Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Future
Sarepta Therapeutics’ recent market decline reflects a confluence of factors. The nuanced scientific and regulatory journey of ELEVIDYS, broader macroeconomic pressures on biotech, an increasingly complex intellectual property landscape, and emerging geopolitical and cybersecurity risks all play a role. The company’s trajectory will depend on its ability to navigate these multifaceted challenges. Securing broader regulatory approvals, managing its cost structure, and strategically diversifying its pipeline are critical steps.
Sarepta, as a prominent player in the gene therapy space, particularly for DMD, has its successes and failures closely watched by investors and other companies. The challenges Sarepta faces- such as AAV vector issues, regulatory scrutiny on accelerated approval, safety warnings, and manufacturing complexity-are not unique to Sarepta 12 13. They represent systemic risks for the entire gene therapy industry. Sarepta’s experience, therefore, serves as a cautionary tale and a bellwether for the sector’s broader maturity and investment climate. How Sarepta navigates these challenges and whether it ultimately achieves widespread commercial success for ELEVIDYS will likely influence investor appetite and regulatory approaches for other gene therapy companies. This will impact the overall growth trajectory of this high-potential but high-risk therapeutic modality.
References
- Investment Strategy – March 2025 – BMO Wealth Insights
- Sarepta Voluntarily Pauses All Shipments of DMD Gene Therapy
- ELEVIDYS Update – Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD)
- FDA Shuts Down Sarepta’s Distribution of Gene Therapy Elevidys
- FDA Suspends Muscular Dystrophy Drug After 3 Patient Deaths
- 5 questions on Sarepta, the FDA and a Duchenne gene therapy crisis | BioPharma Dive
- Sarepta Therapeutics Announces Topline Results from EMBARK
- Safety and efficacy of delandistrogene moxeparvovec versus placebo in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Phase 3 EMBARK primary result
- Duchenne patient dies after receiving Sarepta gene therapy | BioPharma Dive
- Sarepta Therapeutics Announces Strategic Restructuring and…
- Overcoming Challenges in AAV- and rAAV-based Gene Therapies
- AAV Vector Production Challenges Drive Innovation in Gene
- EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen) | Treatment of Duchenne Muscular
- Exondys 51 (eteplirsen) FDA Approval History – Drugs.com
- VYONDYS 53 (golodirsen) | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Treatment
- VYONDYS 53® – Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy
- AMONDYS 45 (casimersen)
- Casimersen (AMONDYS 45™): An Antisense Oligonucleotide for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy – PMC – PubMed Central
- Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. Sued for Securities Law Violations
- Behind the Case: How Latham & Finnegan Secured $115m Biotech
- The Inflation Reduction Act Is Negotiating the United States Out of …,
- FAQs about the Inflation Reduction Act’s Medicare Drug Price
- Sarepta Therapeutics to cut 500 jobs amid restructuring
- Sarepta Announces Restructuring as It Lays Off 500 Employees
Sarepta Therapeutics Short (sell)
Enter At: 12.86
T.P_1: 11.84
T.P_2: 9.90
T.P_3: 7.63
T.P_4: 5.85
T.P_5: 3.38
T.P_6: 1.16
S.L: 18.24