Rocket Lab, a publicly traded company (RKLB), has rapidly emerged as a significant force in the commercial space industry. It operates as a vertically integrated, end-to-end space company. This comprehensive approach means Rocket Lab handles everything from launch services to spacecraft manufacturing and component production. The company’s multifaceted capabilities position it uniquely within the burgeoning space sector.
Headquartered in Long Beach, California, Rocket Lab maintains manufacturing facilities in both the United States and New Zealand. Its global operations also include strategically located launch sites in New Zealand and Virginia, USA. This dual-nation presence provides considerable operational flexibility and distinct strategic advantages. Being a US-headquartered company with a US launch site is particularly critical for securing sensitive US government and national security contracts. This structure directly addresses the US government’s desire for domestic, resilient supply chains and assured access to space. This dual-nation presence, especially the strong US footprint, differentiates Rocket Lab from many international competitors. It positions the company as a trusted partner for Western allies, particularly in an era of increasing geopolitical competition, thereby reducing perceived supply chain risks for critical missions.
This article will delve into the complex interplay of global trends that have propelled Rocket Lab’s growth. It explores how geopolitical shifts, macroeconomic forces, and the changing state of the world have shaped the company’s trajectory. The analysis will demonstrate Rocket Lab’s strategic importance through geopolitical, geostrategic, and macroeconomic lenses.
The New Space Paradigm: A Strategic Imperative
The global space economy is undergoing a dramatic transformation. It is projected to grow from $630 billion in 2023 to an impressive $1.8 trillion by 2035. This exponential growth is primarily driven by the increasing commercialization of space. Decreasing costs of launch and satellite technology, coupled with significant private investment, are fueling this expansion. New applications are continuously emerging, creating diverse market opportunities across various sectors.
Space has evolved into a critical domain for national security and economic prosperity. It is no longer solely the purview of government agencies but a vital arena for global competition. This fundamental shift necessitates reliable, resilient, and responsive access to space infrastructure. Commercial companies are now central to national space strategies. Governments are increasingly leveraging commercial capabilities to enhance national security and strategic advantage. This approach allows for faster innovation, lower costs, and greater resilience compared to traditional government-led programs. It also enables diversification of capabilities beyond a few state-controlled entities. This dynamic creates a significant market opportunity for agile, commercially driven companies like Rocket Lab. They can serve both commercial clients and critical national security missions, blurring the lines between the two sectors and expanding their addressable market.
Geopolitical Gravity: Rocket Lab’s Strategic Positioning
The ongoing US-China rivalry significantly influences the space sector. The United States actively seeks to establish domestic and resilient space supply chains. This reduces dependence on foreign entities for critical space components and launch services. Space is recognized as a vital domain for national security, intelligence gathering, and military operations. The US government prioritizes responsive and reliable access to space.
Rocket Lab, as a US-headquartered company with US manufacturing and launch capabilities, directly benefits from these strategic imperatives. It performs critical missions for agencies like the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and the US Space Force (USSF). The ability to provide a responsive launch, enabling rapid deployment or reconstitution of assets, is paramount for military and intelligence operations. Electron’s dedicated launch capability directly addresses this critical need.
Rocket Lab’s vertical integration provides a high degree of supply chain security and control for national security clients. This minimizes risks associated with foreign dependencies, intellectual property concerns, or potential sabotage, which are major concerns in a competitive geopolitical landscape. It also ensures the integrity and trustworthiness of components used in sensitive missions. This strategic advantage creates a significant competitive moat for Rocket Lab, particularly against companies with less integrated supply chains or those heavily reliant on foreign components. It positions Rocket Lab as a preferred, low-risk partner for critical government contracts, securing a stable revenue stream less susceptible to market fluctuations.
Responsive launch extends beyond mere speed; it represents a crucial strategic capability. In a contested space environment, the capacity to rapidly replace damaged satellites or deploy new assets provides tactical flexibility and strengthens national deterrence. This capability is vital for maintaining persistent surveillance, secure communications, and precision navigation. This elevates responsive launch from a niche service to a critical strategic asset. It drives sustained demand from national security agencies, offering Rocket Lab a high-value, defensible market segment less price-sensitive than pure commercial ventures.
Macroeconomic Tailwinds: Fueling Commercial Space Growth
The commercialization of space is a powerful macroeconomic trend. This is driven by decreasing launch costs and increasing demand for satellite data across various sectors. The small satellite market is experiencing significant growth. This growth is fueled by demand for Earth observation, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and global communications. Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is ideally suited for this burgeoning market segment.
Venture capital and private investment continue to flow into space technology companies. Rocket Lab’s successful public listing (RKLB) validates the market’s confidence in the sector’s long-term potential. The space industry contributes significantly to economic growth, creating high-tech jobs and driving innovation across various sectors. This broader economic impact aligns with national economic development goals.
The proliferation of small satellites creates demand across the entire space value chain. This includes satellite buses, components, and on-orbit services. This broader demand underpins Rocket Lab’s strategic expansion into space systems and its acquisition strategy. The company’s space systems revenue is bolster its in-house manufacturing capabilities. By diversifying beyond launch services into higher-margin space systems, the company reduces reliance on a single revenue stream. This makes the company more financially resilient to fluctuations in launch demand or increased competition in the launch market, enhancing its attractiveness to financial investors.
Sustained investor confidence and capital inflow generate a self-reinforcing cycle. This funding empowers companies like Rocket Lab to invest significantly in research and development, scale their operations, and pursue strategic acquisitions. This influx of capital also attracts top talent and fosters a dynamic ecosystem, reinforcing the sector’s growth trajectory. Rocket Lab’s ability to attract and leverage this capital provides a significant competitive advantage. It allows the company to develop next-generation technologies, such as Neutron, expand its infrastructure, and potentially outpace less well-funded competitors, solidifying its market leadership.
Global Space Economy Projections & Small Satellite Market Growth
The following table illustrates the significant growth trajectory of the space economy and the small satellite market, highlighting the robust macroeconomic tailwinds supporting companies like Rocket Lab.
| Metric | Year | Value | Growth Drivers |
| Global Space Economy Size | 2023 | $630 Billion | Commercialization, Decreasing Costs, Demand for Data |
| Global Space Economy Size | 2035 | $1.8 Trillion | Commercialization, Decreasing Costs, Demand for Data |
| Small Satellite Market | Ongoing | Significant Growth | Earth Observation, IoT Connectivity, Global Communications |
Note: Specific numerical projections for the small satellite market beyond “significant growth” were not provided in the source material, but the trend is clear.
Rocket Lab’s Differentiated Edge: Technology and Vertical Integration
Rocket Lab’s core strength lies in its diverse technological portfolio and vertical integration. This full-stack approach encompasses launch services, spacecraft manufacturing, and component production.
Electron: This small-lift rocket has achieved over 40 launches with a 91% success rate, making Rocket Lab the only US small launch provider with a consistent cadence. Electron is specifically designed for dedicated small satellite launches. Its reliability is a critical competitive advantage, particularly for sensitive national security payloads.
Photon: This high-performance satellite bus is versatile, supporting various missions from Low Earth Orbit (LEO) to lunar and interplanetary destinations. Photon is key to Rocket Lab’s strategy to grow its space systems revenue, which is expected to surpass launch revenue.
Neutron: This medium-lift, reusable rocket is under development. It is designed to target the growing market for mega-constellations, human spaceflight, and deep space missions. Neutron’s reusability aims to significantly reduce launch costs and increase cadence.
Rocket Lab’s strategic acquisition of companies like SolAero, Sinclair Interplanetary, and PSC further enhances its vertical integration. This strategy strengthens its in-house capabilities across the entire space value chain.
Rocket Lab’s vertical integration offers significant operational advantages. By designing and manufacturing most components internally, the company maintains stringent quality control, optimizes production processes, and reduces lead times. This directly contributes to Electron’s high reliability and enables faster iteration and development cycles for new technologies like Neutron. It also allows for more effective cost management by eliminating third-party markups. This integrated approach cultivates a reputation for reliability and quality, which is paramount in the high-stakes space industry. This trust translates into stronger customer relationships, particularly with government and defense clients who prioritize mission success above all else. It also supports the long-term viability of reusability efforts by ensuring component durability and consistent performance.
Neutron’s reusability represents a strategic move to unlock new economic models in space. By drastically reducing the cost per launch, it makes large-scale constellation deployment more economically viable for both commercial entities and governments. This increased affordability and cadence are critical for building out the next generation of space infrastructure and for enabling more frequent human spaceflight missions. It positions Rocket Lab to capture a significant share of the rapidly expanding medium-lift market, directly challenging established players. Success with Neutron’s reusability could solidify Rocket Lab’s position as a leader in cost-effective, high-cadence launch services. This capability is essential for the long-term growth of the space economy, particularly as demand for massive satellite constellations and more complex missions intensifies. It could also open doors to entirely new business models, such as on-orbit servicing or in-space manufacturing, by making access to space more routine and affordable.
Rocket Lab’s Key Capabilities and Milestones
The following table summarizes Rocket Lab’s core technological assets and their strategic significance.
| Product/Service | Description/Purpose | Key Stats/Milestones | Competitive Advantage |
| Electron | Small lift launch vehicle | 40+ Launches, 91% Success Rate | Reliable, Responsive, Dedicated small satellite launch |
| Photon | High-performance satellite bus | Versatile (LEO to lunar/interplanetary missions) | Supports diverse missions, Key to space systems growth |
| Neutron | Medium-lift, reusable rocket (under development) | Targets mega-constellations, human spaceflight | Aims for cost-effective, high-cadence launch |
| Space Systems | Satellite manufacturing, components, on-orbit services | Expected revenue to surpass launch revenue | Full-stack provider, Vertical integration |
From Launch to Orbit: Expanding Capabilities and Market Share
Rocket Lab’s strategy extends beyond launch services to becoming an end-to-end space solutions provider. The company’s space systems revenue is projected to surpass its launch revenue. This expansion is driven by a robust acquisition strategy, integrating companies like SolAero (solar cells), Sinclair Interplanetary (satellite components), and PSC (satellite separation systems). These acquisitions bolster its in-house manufacturing capabilities.
The demand for satellite constellations, such as Starlink and Kuiper, is driving the need for reliable launch and efficient satellite manufacturing. Rocket Lab’s full-stack approach directly addresses this growing demand for space infrastructure. Strategic partnerships, such as those with Lockheed Martin, MDA, and Varda Space Industries, demonstrate trust in Rocket Lab’s capabilities and expand its market reach. These collaborations validate its technology and operational excellence.
Rocket Lab’s acquisition strategy is a deliberate effort to capture a larger share of the burgeoning space infrastructure market. By acquiring key component manufacturers, the company reduces its reliance on external suppliers, gains control over critical technologies, and can offer a more integrated, cost-effective solution to clients building large constellations. This positions Rocket Lab as a comprehensive provider, simplifying procurement and integration for customers. This aggressive vertical integration through acquisition establishes a significant barrier to entry for competitors. New entrants would need to replicate Rocket Lab’s extensive in-house capabilities or rely on less integrated, potentially more expensive, supply chains. This strategy solidifies Rocket Lab’s competitive advantage and allows for greater control over pricing and delivery schedules.
Collaborations with established aerospace and defense giants like Lockheed Martin serve as powerful endorsements of Rocket Lab’s technology, reliability, and strategic importance. These partnerships provide access to larger contracts, broader market segments, and often involve sharing expertise, accelerating Rocket Lab’s own development. They signal to other potential clients and investors that Rocket Lab is a credible and capable partner for complex, high-value missions. These collaborations can also serve as springboards for future growth. They expose Rocket Lab to cutting-edge requirements and potentially lead to joint ventures or deeper integrations into major defense programs, securing long-term revenue streams and positioning the company at the forefront of future space initiatives.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
The space industry remains highly competitive. Rocket Lab faces competition from established players like SpaceX (Falcon 9, Starship), ULA, and Arianespace, as well as numerous emerging small launch providers. Navigating the complex and evolving regulatory environment is a continuous challenge for all space companies. Adherence to national and international space laws is crucial for operations.
Intense competition, particularly from SpaceX’s cost-effective reusability, compels all industry participants, including Rocket Lab, to innovate rapidly. This competitive pressure drives down costs, improves efficiency, and accelerates technological advancements across the industry. This dynamic also suggests a potential future for consolidation within the small launch market as less differentiated players struggle to compete on price or cadence. Rocket Lab’s vertical integration and expansion into space systems are direct responses to this competitive environment. By offering a comprehensive solution, the company aims to differentiate itself beyond just launch, establishing a more resilient business model less vulnerable to pure launch price wars. This strategy positions them to thrive even in a consolidating market.
While navigating the complex space regulatory environment presents a continuous challenge, its inherent complexity also acts as a significant barrier to entry for new or less experienced players. Established companies like Rocket Lab, with their proven track record of successfully navigating these complexities and maintaining strong relationships with regulatory bodies, possess a distinct operational advantage. Their existing launch licenses and operational history reduce risk for clients. This regulatory barrier contributes to market stability by limiting the influx of unproven competitors. It allows established players to solidify their market positions and invest with greater certainty, knowing that the playing field is not easily disrupted by fly-by-night operations. Rocket Lab’s compliance and operational maturity become a selling point for risk-averse clients, particularly government agencies.
Despite these challenges, significant opportunities for future growth exist. Rocket Lab is exploring emerging areas such as on-orbit servicing, space debris removal, and in-space manufacturing. These areas represent the next frontier of the space economy.
Conclusion: Rocket Lab’s Enduring Gravitas in the New Space Race
Rocket Lab has strategically positioned itself as a critical player in the evolving space economy. Its rise is a direct reflection of profound shifts in geopolitics, macroeconomics, and global strategic priorities. The company’s vertical integration, reliable launch services, and expanding space systems capabilities provide a robust competitive advantage. These assets directly address the increasing demand for resilient, domestic, and responsive space infrastructure. By capitalizing on the commercialization of space, the booming small satellite market, and robust investment trends, Rocket Lab is poised for continued growth. Its future endeavors in areas like on-orbit servicing will further solidify its long-term relevance. Rocket Lab stands as a testament to the power of innovation and strategic foresight. It effectively navigates complex global currents to secure its place at the forefront of the new space race.
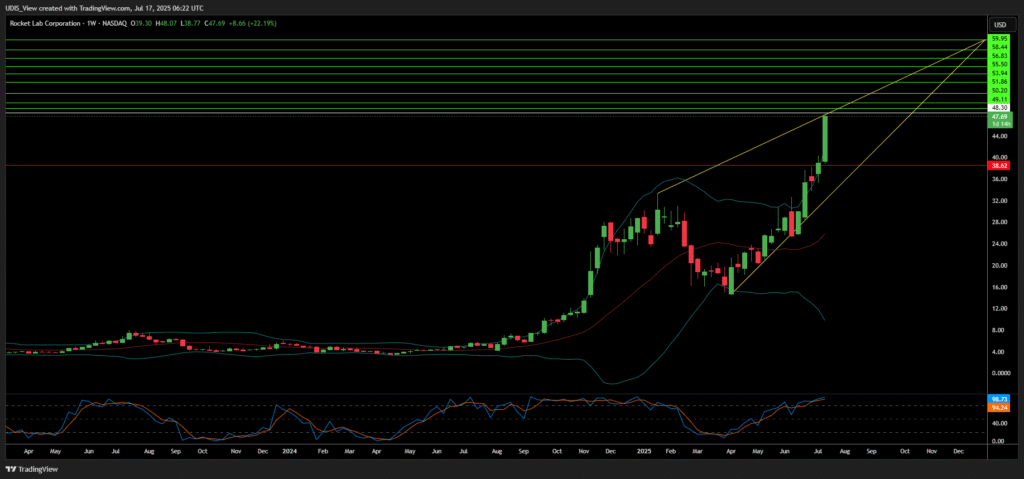
Rocket Lab Long (Buy)
Enter At: 48.30
T.P_1: 49.11
T.P_2: 50.20
T.P_3: 51.86
T.P_4: 53.94
T.P_5: 55.50
T.P_6: 56.83
T.P_7: 58.44
T.P_8: 59.95
T.P_9: 61.82
S.L: 38.62